Jacob, 1979; Ambraseys and Melville, 1982). The earthquake was felt in Karachi, Pakistan, where ground motions (figure 2) lasted approximately 30 seconds, stopping the clock in the Karachi Municipality Building and interrupting the communication cable link between Karachi and Muscat off Pakistan's Makran Coast (Balochistan) generated a destructive tsunami in the Northern Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean. More than 4,000 people were killed along the Makran Coast of Pakistan by both the earthquake and the tsunami.
The tsunami reached a height of 17m(50 feet) in some Makran ports and caused great
damage to the entire coastal region. A good number of people were washed away. The
tsunami was also recorded at Muscat and Gwadar.
The damage from the earthquake was great, but the greatest destruction to the region was caused by the tsunami that was generated. Tsunami waves "swept the whole of the Arabian Sea coast" .
The fishing village of Khudi, Pakistan and its entire population, 48 km west of Karachi, was swept away.
Tsunami has been observed in the North Indian Ocean on the Iranian coast
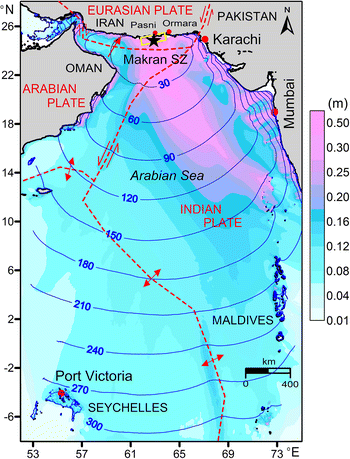
Karachi effects of the Makran earthquake and tsunami of November 1945
The effects of the earthquake and tsunami on 28 November 1945 sourced near the Makran coast of the Arabian Sea are captured in a new UNESCO-IOC publication entitled Karachi effects of the Makran earthquake and tsunami of November 1945. (Select image below to view publication).
The event registered abundantly at Karachi, the port city nearest the earthquake source and disturbed port facilities and fishing villages to the east of Karachi Harbour. The new publication includes archives from this event: a lighthouse notebook, tide-gauge record, local newspapers, large-scale maps, and photographs complimenting previously published eyewitness testimory gathered in 2014-2018.
It is hoped that the stories and
information captured in this new publication will inform precautions
against natural hazards in Karachi and beyond. A tsunami like the one in
1945 would today encounter more people and developed property in
Karachi's port areas with seaside populations and shipping increased
tenfold or more since 1945.
The tsunami reached as far south as Mumbai. Bombay Harbor, Versova (Andheri), Haji Ali (Mahalaxmi), Juhu (Ville Parle) and Danda (Khar). In Mumbai the height of the tsunami was 2 meters. Fifteen (15) persons were washed away.
According to reports the first wave was observed at 8:15am (local time) on Salsette Island in Mumbai (3). There was no report on damage at Bombay Harbor.
Five people died at Versova (Andheri, Mumbai), and six more at Haji Ali (Mahalaxmi, Mumbai), Several fishing boats were torn off their moorings at Danda and Juhu.
| Date |
Location
|
1524 1762 1819 1847 1881 1883 1941 1945 |
Near Dabhol, MaharashtraAn earthquake occurred during 1524 A.D. off the coast of Dabhol, Maharashtra and. a resulting large tsunami caused considerable alarm to the Portuguese fleet that was assembled in the area (Bendick and Bilham, 1999).
West Bengal and Orissa due to quake at Arakan Coast, Myanmar West coast of India due to quake at Rann of Kutch, Gujarat Great Nicobar Island Car Nicobar Island On the east coast, due to Krakatoa eruption On the east coast due to eruptions at Andaman Islands On the west coast of India including Mumbai due to a quake at Merkan Coast, Baluchistan |
The India tectonic plate has been drifting and moving in a north/northeast direction, for millions of years colliding with the Eurasian tectonic plate and forming the Himalayan Mountains.
(USGS graphic showing the migration of the Indian tectonic plate)
Satellite photo of a section of the Makran rugged and tectonic coastline showing uplifted terraces, headlands, sandy beaches, mud flats, rocky cliffs, bays and deltas. Numerous mud volcanoes are present along the shores.
==================================================
==============================================================================================
Potential[future] Tsunami Generating Sources Along the Makran Seismic Zone and Bombay
A factor that could contribute to the destructiveness of a tsunami along the Makran coastline would be the relatively large astronomical tide, which is about 10-11 feet.
A tsunami generated during high tide
 |
| High tide |
would be significantly more destructive; FOR mumbai CITY.
LATEST NEWS:-Magnitude 7.2 earth quake in - SOUTHWESTERN PAKISTAN ---2011 January 18
soon MUMBAI BEACHES MAY GET COVERED BY SEA WATER
| HIGH TIDE +TSUNAMI |
- A tsunami is a series of waves - the first may not be the largest
- Wave heights cannot be predicted and can vary along a coast due to local effects
- The time from one tsunami wave to the next can be five minutes to an hour
The monster 8.9-magnitude earthquake which hit Japan was the country's biggest ever and the seventh largest on record, according to US Geological Survey data.
Here are the largest magnitude earthquakes in history, according to the USGS website:
9.5, Chile, May 5, 1960
A quake off the coast of southern Chile killed more than 1,600 people and left 2,000,000 homeless.
A quake and tsunami killed 128 people and caused severe damage to the state's largest city Anchorage.
9.1, Indonesia, December 26, 2004
An undersea quake caused a massive tsunami that devastated coastlines in countries around the Indian Ocean, ultimately killing more than 220,000 people.
9.0, Russia, November 4, 1952
A quake off the coast of the remote Kamchatka peninsula in Russia's far east caused Pacific-wide tsunamis.
9.0, Peru, August 13, 1868
The port of Arica, which is now part of Chile, was hit by a quake felt up to 1,400 kilometres (870 miles) away.
9.0, North America, January 26, 1700
A quake affecting 1,000 kilometres of coastline set off a tsunami that crossed the Pacific Ocean and caused damage to coastal villages in Japan.
8.9, Japan, March 11, 2011
An undersea quake off northeast Japan unleashed a 10-metre-high tsunami which left devastation in its wake.
8.8, Chilean coast, February 27, 2010
An offshore quake and tsunami killed more than 500 people, most in the coastal area of Maule, 400 kilometres (250 miles) south-west of the capital Santiago.
8.8, Ecuador, January 31, 1906
A quake struck off the coast of Ecuador and Colombia and was felt as far away as San Francisco.
8.7, Alaska, February 4, 1965
A quake in the remote Rat Islands generated a tsunami reported to be 10 metres high.
8.7, Portugal, November 1, 1755
The capital Lisbon was struck by a quake while many residents were in church. A quarter of the city's population perished.
8.7, Chile, July 8, 1730
A quake hit the city of Valparaiso, 120 kilometres northwest of the capital Santiago, causing a tsunami which hit more than 1,000 kilometres of coastline.
More than 300 dead and more than 500 are feared missing in the massive earthquake that struck Japan on Friday, March 11, 2011. There has been widespread loss to infrastructure, the coastal areas of Japan being the worst affected.
Year Month Intensity (MMI)/Magnitude (R)
1618 May IX MAGNITUDE (9) IS VERY VERY SEVERE EARTH QUAKE LUCKLY BEFORE CITY WAS MADE
1832 Oct VI MAGNITUDE(7) IS SEVERE EARTH QUAKE
1906 March VI MAGNITUDE (6) IS ALSO SEVERE
1929 February V MAGNITUDE (5)
1933 July V MAGNITUDE (5)
1951 April VIII MAGNITUDE (8) VERY SEVERE
1966 May V (5)
1967 April 4.5 (R)
1967 June 4.2 (R)
1993 September 6.4 (R)
1998 May 3.8
2005 March 5.1
2005 June 3.7
2005 August 4.1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Japanese tsunami
======================================================================
India | Posted on Apr 12, 2012 at 12:55pm IST
Mumbai is tsunami-proof, says civic official[FOOLISH TALK ]
According to a senior BMC official, "Studies and experts assert that tsunami can never hit Mumbai, as there isn't any epicenter in the ocean on the western side. It’s only earthquakes that can bother the city because there are three major active fault lines in Panvel, Koyna and another spot, which is in Pakistan.”
Chief officer of BMC’s Disaster Management Cell M Narvekar said, “Though there was no alert in Mumbai, as per the norms, we had kept all the facilities on a stand-by. Also, we were constantly taking details from INCOIS, which is the central nodal agency and gives accurate hourly updates.”
Likewise, civic body’s Standing Committee Chairman Rahul Shewale said, “We are prepared for disasters like buildings collapse during rains and earthquake. In case of an emergency, we’d have activated the ward-level disaster controls following which 256 fire engines, 30 ambulances, along with several private ambulances would have been sent to help people.”



No comments:
Post a Comment