History
city consisted of seven islands namely Colaba, Mazagaon, Old Woman's Island, Wadala, Mahim, Parel, and Matunga-Sion. Although the signs of human life were found since the Stone Age,

,Gilbert Hill-Andheri west:-http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.in/2012/06/gilbert-hill-andheri-west.html
Gilbert Hill is a 60 m (197 ft) monolith column of black basalt rock in Andheri, inMumbai, India. The rock has a sheer vertical face and was formed when molten lava was squeezed out of the Earth's clefts during the Mesozoic Era about 65 million years ago. During that era, molten lava had spread around most of the Indian states of Maharashtra,Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh, covering an area of 50,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi). The volcanic eruptions were also responsible for the destruction of plant and animal life during that era.
volcanoes near Mumbai dinosaurshttp://www.livescience.com/25324-volcanoes-killed-dinosaurs.html
The people of fishermen community called koli dominated the island..
The people of Kolis community were the separate groups of tribes from Vindhya Plateau, Gujarat, and Konkan. During that period theregenerally three-four major tribes in the region.
| Map of "Bharatvarsha" (Kingdom of India) during the time of Mahabharata and Ramayana. (Title and location names are in English |
| Buddist stupa at Nala sopara |
Nala Sopara
In ancient times, it was the largest township on India's west coast, trading with Mesopotamia, Egypt, Cochin, Arabia and Eastern Africa. Proof of Ashokan inscriptions have also been recovered from Sopara, Buddhist text gives details that is was a prominent Buddhist area. During excavation ruins of a Buddhist Stupa were found. From the center of the stupa (inside a brick built chamber) a large stone coffer was excavated which contained eight bronze images of Maitreya Buddha which belong to the 8th-9th century A.D. The coffer contained a relic caskets, numerous gold flowers and fragments of a begging bowl. A silver coin of Gautamiputra Satakarni was also found from the mound. Later the area of captured by the Mauryans in 250 B.C. Origin of Mumbai can be well understood by dividing the history of its evolution into different period.
The Period of Several Rulers: Mauryan Empire Ashoka captured the area from Kolis community and established his dominance during 350 B.C

| Buddhist proselytism at the time of kingAshoka (260–218 BCE) |
It is the emblem of India.

Koyikkal Palace │India Tourism│Kerala ...
Nearly 374 Roman gold coins, each worth up to five hundred thousand rupees today, depicting Roman gods and goddesses like Venus, Hercules, Mars, Ceres, Genius, etc and rulers like Hardin (AD 117 - 138) are also among the collection.eveidence of ancient roman trade with india

A Short Sketch of the Early History of the Town and Island of Bombay:http://archive.org/stream/ashortsketchear00joshgoog#page/n3/mode/2up
The Elephanta Caves:-http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elephanta_Caves

The islands were incorporated into the Maurya Empire under Emperor Ashoka of Magadha in the third century BCE. The empire's patronage made the islands a centre of Hindu and Buddhist religion and culture.[5] Buddhist monks, scholars, and artists created the artwork, inscriptions, and sculpture of the Kanheri Caves in the mid third century BCE[8] and Mahakali Caves.[9] After the decline of the Maurya Empire around 185 BCE, these islands fell to the Satavahanas.[10] The port of Sopara (present-day Nala Sopara) was an important trading centre during the first century BCE,[11] with trade contacts with Rome.[12] The islands were known as Heptanesia (Ancient Greek: A Cluster of Seven Islands) to the Greek geographer Ptolemy in 150 CE.[13] After the end of the Satvahana rule in 250 CE, the Abhiras of Western Maharashtra and Vakatakas of Vidarbha held dominion over the islands. The Abhiras ruled for 167 years, till around 417 CE.[10] The Kalachuris of Central India ruled the islands during the fifth century,[14] which were then acquired by the Mauryas of Konkan in the sixth and early part of the seventh century.[10] The Mauryas were feudatories of Kalachuris,[10] and the Jogeshwari Caves were constructed during their regime between 520 to 525.[15] The Greek merchant Cosmas Indicopleustes visited Kalyan (near Mumbai) during 530–550.[16] The Elephanta Caves also dates back to the sixth century.[17] Christianity arrived in the islands during the sixth century, when the Nestorian Church made its presence in India.[18] The Mauryan presence ended when the Chalukyas of Badami in Karnataka under Pulakesi II invaded the islands in 610.[19] Dantidurga of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty of Karnataka conquered the islands during 749–750.[10]
The Silhara dynasty of Konkan ruled the region between 810 and 1260.[20] The Walkeshwar Temple was constructed during the 10th century[21] and the Banganga Tank during the 12the century under the patronage of the Silhara rulers.[22] The Italian traveler Marco Polo's fleet of thirteen Chinese ships passed through Mumbai Harbour during May — September 1292.[16][23] King Bhimdev founded his kingdom in the region in the late 13th century[24] and established his capital in Mahikawati (present day Mahim).[25] He belonged to either the Yadava dynasty of Devagiri in Maharashtra or the Anahilavada dynasty of Gujarat.[24] He built the first Babulnath temple in the region and introduced many fruit-bearing trees, including coconut palms to the islands.[26] The Pathare Prabhus, one of the earliest settlers of the city, were brought to Mahim from Patan and other parts of Saurashtra in Gujarat around 1298 by Bhimdev during his reign.[27] He is also supposed to have brought Palshis,[28] Pachkalshis,[28] Bhandaris, Vadvals, Bhois, Agris and Brahmins to these islands. After his death in 1303, he was succeeded by his son Pratapbimba, who built his capital at Marol in Salsette, which he named Pratappur. The islands were wrested from Pratapbimba's control by Mubarak Khan, a self-proclaimed regent of the Khilji dynasty, who occupied Mahim and Salsette in 1318. Pratapbimba later reconquered the islands which he ruled till 1331. Later, his brother-in-law Nagardev for 17 years till 1348. The islands came under the control of the Muslim rulers of Gujarat in 1348, ending the sovereignty of Hindu rulers over the islands.[10]

and Pahlavas (Indo-Parthians),... who rooted the Khakharata family (The Kshaharata family of Nahapana); who restored the glory of the Satavahana race[12]Gautamiputra Satakarni may also have defeated Shaka king Vikramaditya in 78 BCE and started the calendar known as Shalivahana era or Shaka era, which is followed by the Gujarati, Marathi, Kannadiga and Telugu people and is the Indian National Calendar.
and abolished the control of Mauryas from the area
Chalukya Territories during Pulakesin II c. 640 C.E
The Parel Heptad;The incomplete 6th Century statue is an indicator of both, the ancient civilisation that once resided in Parel village and the ignorance of those who reside in Mumbai at present

With the passing time the area came under the control of the rulers of Silhara dynasty of Konkan during 810 to 1260.The Hindu
Silhara dynasty ruled the region
The genealogy of this branch of the Shilaharas ruling over North KONKAN:-

[ Nyaya gaon became present Naigaon]
and Brahmins to these islands. The Bhandaris were originally toddy trappers; the Vadvals were gardeners. He introduced many fruit-bearing trees, including coconut palms to the island.
However with the invasion of area by Muslim rulers of Gujarat in 1348 the dominance of Hindu rulers came to an end.
The Mughal Period:
The Muslim ruler Mubarak Khan of Khaliji dynasty
of Gujaratcaptured the area from the Hindu rulers and established his dominance on the islands.
He appointed Maliq-us-Sharq as the governor of Mahim
and entrusted him the authority to make survey of existing rules in the islands and also amended the existing revenue system of the island. However, during the early
15th century the Bhandaris captured the island from the Mughal rulers and controlled the area for eight years.
After which the area was recaptured by Rai Qutb of Gujarat Sultanate.
After the death of Rai Qutb the area came
under the control of Ahmad Shah I Wali of BahmaniSultanate.
After the decline of Ahmad Shah I the sultanate of Gujarat recaptured the area and established
during his dominance and constructed various mosques the major being the mosque of famous saint Haji Ali called as Haji Ali Dargah
and Mahim daragah
.
However with the invasion by Portuguese the rule of Mughal emperors came to an end
.
brought these islands to Charles II of England
as part of her marriage dowry.
WILD ANIMALS IN BOMBAY http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010/06/how-mumbai-lost-its-animal-instinct.html
.

This gold coin reveals the veiled head of Julius Caesar on the front side with emblem "CAESAR COS TER
THE MONTHS OF JULY AND AUGUST ARE NAMED IN THEIR HONOR
Roman Gold Coin – Augustus Aureus. ceasar
Gold Coin of Julius Caesar:-
This gold coin reveals the veiled head of Julius Caesar on the front side with emblem "CAESAR COS TER
BECAUSE ROMAN EMPIRE TRADED WITH OTHER COUNTRIES; MOSTLY WITH GOLD COINS ,THERE ARE STILL CHANCES OF FINDING ROMAN GOLD COINS IN SOPARA / NALA SOPARA
| roman ship used for trade with india |
one can see hundreds of ancient roman gold coins at -Koyikkal Palace, Thiruvananthapuram
|
Location :Nedumangad, about 18 km from Thiruvananthapuram
city on the way to the Ponmudi hill station and the Courtalam waterfalls, Thiruvananthapuram district, south Kerala. Attractions :Palace, folklore museum and numismatics museum. Visiting hours : 9:00 am to 5:00 pm on all days, except Mondays. |

Koyikkal Palace │India Tourism│Kerala ...
travelsntourism.com
Nearly 374 Roman gold coins, each worth up to five hundred thousand rupees today, depicting Roman gods and goddesses like Venus, Hercules, Mars, Ceres, Genius, etc and rulers like Hardin (AD 117 - 138) are also among the collection.eveidence of ancient roman trade with india
The Kanheri Caves
are a group of rock-cut monuments, located north of Borivali on the western outskirts of Mumbai, India, deep within the green forests of the Sanjay Gandhi National Park. It is 6 km from the National Park Main Gate & 7 km from Borivali Station. Tourists can go in after 7.30 a.m. Kanheri Caves are signs of Buddhist influence on art and culture in India. Kanheri comes from the Sanskrit word Krishnagiri generally meaning black in colour
These caves date from 1st century BCE to 10th century CE. In total in the basalt there have been carved 109 caves. Unlike the elegant splendor of Elephanta Caves nearby, the earlier cells are spartan and unadorned. Each cave has a stone plinth for a bed. A congregation hall with huge stone pillars contains the stupa, a Buddhist shrine. Farther up the hill are the remains of an ancient water system, canals and cisterns that collected and channeled the rainwater into huge tanks.[3]Once the caves became permanent monasteries, they began to be carved out of the rock with intricate reliefs of Buddha and the Bodhisattvas carved into the walls. Kanheri had become an important Buddhist settlement on the Konkan coast by the 3rd century A.D.
This area of was developed as the merging point of two religions namely Hinduism and Buddhism. Various manuscripts and works of fine arts related to Buddhism can be witnessed in the
| the caves are inside national park named agter sanjay gandhi |
Videos |
| inside sanjay gandhi national park there is an enclosed space called lion safari park |
A depiction of a framed male alongside the entrance to one of the caves.
sanjay gandhi national park -the only national park inside a major city any where in the world
Toy train at Sanjay Gandhi Biological park
 hindustantimes.com  indiasendangered.com |
This prayer room at Kanheri, Mumbai, was carved out of one single rock in 1st century B.C.! Kanheri Caves had become an important Buddhist settlement on the Konkan coast by the 3rd century A.D.
A Short Sketch of the Early History of the Town and Island of Bombay:http://archive.org/stream/ashortsketchear00joshgoog#page/n3/mode/2up
mahakali Caves
BELOW -ELEPHANTA CAVES
boat to Elephanta island from gate way of india
The islands were incorporated into the Maurya Empire under Emperor Ashoka of Magadha in the third century BCE. The empire's patronage made the islands a centre of Hindu and Buddhist religion and culture.[5] Buddhist monks, scholars, and artists created the artwork, inscriptions, and sculpture of the Kanheri Caves in the mid third century BCE[8] and Mahakali Caves.[9] After the decline of the Maurya Empire around 185 BCE, these islands fell to the Satavahanas.[10] The port of Sopara (present-day Nala Sopara) was an important trading centre during the first century BCE,[11] with trade contacts with Rome.[12] The islands were known as Heptanesia (Ancient Greek: A Cluster of Seven Islands) to the Greek geographer Ptolemy in 150 CE.[13] After the end of the Satvahana rule in 250 CE, the Abhiras of Western Maharashtra and Vakatakas of Vidarbha held dominion over the islands. The Abhiras ruled for 167 years, till around 417 CE.[10] The Kalachuris of Central India ruled the islands during the fifth century,[14] which were then acquired by the Mauryas of Konkan in the sixth and early part of the seventh century.[10] The Mauryas were feudatories of Kalachuris,[10] and the Jogeshwari Caves were constructed during their regime between 520 to 525.[15] The Greek merchant Cosmas Indicopleustes visited Kalyan (near Mumbai) during 530–550.[16] The Elephanta Caves also dates back to the sixth century.[17] Christianity arrived in the islands during the sixth century, when the Nestorian Church made its presence in India.[18] The Mauryan presence ended when the Chalukyas of Badami in Karnataka under Pulakesi II invaded the islands in 610.[19] Dantidurga of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty of Karnataka conquered the islands during 749–750.[10]
The Silhara dynasty of Konkan ruled the region between 810 and 1260.[20] The Walkeshwar Temple was constructed during the 10th century[21] and the Banganga Tank during the 12the century under the patronage of the Silhara rulers.[22] The Italian traveler Marco Polo's fleet of thirteen Chinese ships passed through Mumbai Harbour during May — September 1292.[16][23] King Bhimdev founded his kingdom in the region in the late 13th century[24] and established his capital in Mahikawati (present day Mahim).[25] He belonged to either the Yadava dynasty of Devagiri in Maharashtra or the Anahilavada dynasty of Gujarat.[24] He built the first Babulnath temple in the region and introduced many fruit-bearing trees, including coconut palms to the islands.[26] The Pathare Prabhus, one of the earliest settlers of the city, were brought to Mahim from Patan and other parts of Saurashtra in Gujarat around 1298 by Bhimdev during his reign.[27] He is also supposed to have brought Palshis,[28] Pachkalshis,[28] Bhandaris, Vadvals, Bhois, Agris and Brahmins to these islands. After his death in 1303, he was succeeded by his son Pratapbimba, who built his capital at Marol in Salsette, which he named Pratappur. The islands were wrested from Pratapbimba's control by Mubarak Khan, a self-proclaimed regent of the Khilji dynasty, who occupied Mahim and Salsette in 1318. Pratapbimba later reconquered the islands which he ruled till 1331. Later, his brother-in-law Nagardev for 17 years till 1348. The islands came under the control of the Muslim rulers of Gujarat in 1348, ending the sovereignty of Hindu rulers over the islands.[10]
With the decline of Mauryas the area came under the control of Satavahanas,:-
The Edicts of Ashoka mention the Sātavāhanas as feudatories of Emperor Ashoka. Fragment of the 6th Pillar Edicts of Ashoka (238 BCE), in Brahmi, sandstone. British Museum.The Satavahanas declared independence some time after the death of Ashoka (232 BCE), as the Maurya Empire began to weaken.
Indian ship on lead coin of Vasisthiputra Sri Pulamavi, testimony to the seafaring and trading capabilities of the Satavahanas during the 1st–2nd century CE.
| Vasisthiputra Sri Pulamavi | |
|---|---|
| Satavahana | |
| Silver coin of Vasisthiputra Sri Pulamavi. British Museum. | |
| Reign | 78–114 CE |
| |||
| Territorial extent of the Satavahana Empire (continuous line), and conquests (dotted line). | |||
who had friendly relations with the kingdom of Rome and developed the port of Sopara (recognized as Nala Sopara later) as the major centre of Trade with Rome. According to the renowned Greek Geographer of the then period Ptolemy the group of islands was called as Heptanesia at that time.
According to the Nasik inscription made by his[Gautamiputra (Sri Yagna) Sātakarni (also known as Shalivahan] mother Gautami Balasri, he is the one......who crushed down the pride and conceit of the Kshatriyas (the native Indian princes, the Rajputs of Rajputana, Gujarat and Central India); who destroyed the Shakas (Western Kshatrapas), Yavanas (Indo-Greeks)
The dynasty was soon extinguished following the rise of its feudatories
,
perhaps on account of a decline in central power
Several dynasties divided the lands of the kingdom among themselves. Among them were:
- [1]Western Satraps in the northwestern part of the kingdom.
- [2]Andhra Ikshvakus (or Srīparvatiyas) in the Krishna-Guntur region.
- (r. 220–320 CE).
- [3]Abhiras in the western part of the kingdom. They were ultimately to succeed the Sātavāhanas in their capital Pratishthānapura .[MODERN DAY PAITHAN TOWN OF MAHARASHTRA STATE]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paithan
- .http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paithan
- [4]Chutus of Banavasi in North Karnataka
- [5]Kadambas of Banavasi in North Karnataka.
- [6]Pallavas of Kanchipuram, of whom the first ruler was Simhavarman I (r. 275–300 CE).
With the decline of Satavahanas, the area felt under the control of rulers of
Abhiras [AHIR]
Abhiras [AHIR]
AHIR KINGS:-
- Ra Mandalika (Ruler of Somnath)
- Ra Graharipu
- Rao Tula Ram
- King Poru
- Rudramurti Ahir
- Madhuriputra (mingled with rajputs)
- Samudragupta]
- Ishwarsena (Western Deccan)
- Virsen (Jalgaon)
{AHIRS OR AHERS OF MAHARASHTRAIN MARUBHUMI (MARWAR), SAURASHTRA AND MAHARASHTRA THEY SERVED THE LOCAL RULERS AND ESTABLISHED THEIR OWN RULE.
ISHWARSENA, A GREAT AHIR GENERAL, BECAME MASTER OF WESTERN DECCAN IN PLACE OF THE FAMOUS SATAVA-HANAS. HE TOOK THE TITLE OF RAJAN AND AN ERA WAS NAMED AFTER HIM.
HIS DESCENDANTS CONTINUED TO RULE FOR NINE GENERATIONS. THERE IS A SIGNIFICANT CONCENTRATION OF [AHER]S IN NORTHERN MAHARASHTRA. THEY ARE VERY INFLUENTIAL IN POLITICS, ADMINISTRATION.
THEY ARE ALL KSHATRIYAS WITH CLASSIFICATION AS 96 KULI MARATHAS SINCE THE ESTABLISHMENT OF HINDAVI SWARAJ BYCHHATRAPATI SHIVAJI.}
and Vakatakas who originated from the areas of Western Maharashtra and Vidharbha respectively.
RULERS OF THE VAKATAKA DYNASTY
- Vindhyasakti (250-270)
- Pravarasena I (270- 330)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vakataka_dynasty
The Pravarapura-Nandivardhana branch
- Rudrasena I (330 - 355)
- Prithvisena I (355 - 380)
- Rudrasena II (380- 385)
- Divakarasena (385- 400)
- Prabhavatigupta (fem.), Regent (385- 405)
- Damodarasena (Pravarasena II) (400- 440)
- Narendrasena (440- 460)
- Prithvishena II (460- 480)
Later in the fifth century the area came under the control of Kalachuris of Central India,. It was during their rule that the
Jogeshwari Caves were constructed.
| Jogeshwari Caves | |
|---|---|
| Middle kingdoms of India | ||||||||||||
| Timeline: | Northwestern India | Northern India | Southern India | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
6th century BCE
5th century BCE 4th century BCE 3rd century BCE 2nd century BCE 1st century BCE 1st century CE 2nd century 3rd century 4th century 5th century 6th century 7th century 8th century 9th century 10th century 11th century |
|
|
| |||||||||
COSMAS INDICOPLEUSTES (LITERALLY "WHO SAILED TO INDIA") OF ALEXANDRIA WAS A GREEK MERCHANTAND LATER MONK PROBABLY OF NESTORIAN TENDENCIES.HE WAS A 6TH CENTURY TRAVELLER, WHO MADE SEVERAL VOYAGES TO INDIA DURING THE REIGN OF EMPEROR JUSTINIAN. HIS TOPOGRAFIA CHRISTIANA (CHRISTIAN TOPOGRAPHY) CONTAINED SOME OF THE EARLIEST AND MOST FAMOUS WORLD MAPSTHE ORIGIN OF WORLD KNOWN ELEPHANTA CAVES DATES BACK TO THE SAME PERIOD.ESTABLISHMENT OF NESTORIAN CHURCH ON THE ISLANDS MARKED THE ARRIVAL OF CHRISTIANS IN THE COUNTRY.
The Chalukyas of Karnataka under Pulakesi II invaded the
area
area
Chalukya Territories during Pulakesin II c. 640 C.E
Pulikesin II exchanges envoys with Sassanaid Khusro II[of Persia-modern day Iran]
ABOVE :-Around 625-26 AD , Chalukya King Pulakesin II (AD 610-42) exchanged envoys with Sassanian(PERSIAN) King Khusrau II (AD 596- 626). The same has been depicted in Ajantha Cave I
The Parel Heptad;The incomplete 6th Century statue is an indicator of both, the ancient civilisation that once resided in Parel village and the ignorance of those who reside in Mumbai at present
Mumbai Mirror
The unfinished sculpture of the seven-headed Shiva
Later during 749-750 A.D. Dantidurga
from
Karanataka captured the island
and established his dominance in the area.
Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta | ||||
| Empire (Subordinate to Badami Chalukyas until 753) | ||||
| ||||
|
Extent of Rashtrakuta Empire, 800 CE, 915 CE
| ||||
| Kailashnath Temple at Ellora, not far from Aurangabad (in modern Maharashtra state), built between about 725-755 |
| Rashtrakuta Kings (753-982) | |
| Dantidurga | (735 - 756) |
| Krishna I | (756 - 774) |
| Govinda II | (774 - 780) |
| Dhruva Dharavarsha | (780 - 793) |
| Govinda III | (793 - 814) |
| Amoghavarsha I | (814 - 878) |
| Krishna II | (878 - 914) |
| Indra III | (914 -929) |
| Amoghavarsha II | (929 - 930) |
| Govinda IV | (930 – 936) |
| Amoghavarsha III | (936 – 939) |
| Krishna III | (939 – 967) |
| Khottiga Amoghavarsha | (967 – 972) |
| Karka II | (972 – 973) |
| Indra IV | (973 – 982) |
| Tailapa II (Western Chalukyas) | (973- |
Shiva sculpture at Ellora Caves.-MADE DURING RASHTRAKUTA KINGS REIGN
With the passing time the area came under the control of the rulers of Silhara dynasty of Konkan during 810 to 1260.The Hindu
Silhara dynasty ruled the region
The genealogy of this branch of the Shilaharas ruling over North KONKAN:-
[1]North Konkan (Thane Branch)
After Rashtrakuta power became weak the last known ruler of this family, Rattaraja, declared his independence. But Chalukya Jayasimha, the younger brother of Vikramaditya, overthrew him and appropriated his possessions. North Konkan was conquered by the Rashtrakuta king Dantidurga sometime in the second quarter of the eighth century.
- Rulers
- Kapardin I (800 – 825)
- Pullashakti (825 – 850)
- Kapardin II (850 – 880)
- Vappuvanna (880 – 910)
- Jhanjha (910 – 930)
- Goggiraja (930 – 945)
- Vajjada I (945 – 965)
- Chhadvaideva (965 – 975)
- Aparajita (975 – 1010)
- Vajjada II (1010 – 1015)
- Arikesarin (1015 – 1022)
- Chhittaraja (1022 – 1035)
- Nagarjuna (1035 – 1045)
- Mummuniraja (1045 – 1070)
- Ananta Deva I (1070 – 1127)
- Aparaditya I (1127 – 1148)
- Haripaladeva (1148 – 1155)
- Mallikarjuna (1155 – 1170)
- Aparaditya II ( 1170 – 1197)
- Ananta Deva II (1198 – 1200)
- Keshideva II (1200 – 1245)
- Ananta Deva III (1245 – 1255)
- Someshvara (1255 – 1265)
[2]second South Konkan (between 765 to 1029),
- Rulers
- Sanaphulla (765 to 795)
- Dhammayira (795 to 820)
- Aiyaparaja (820 to 845)
- Avasara I (845 to 870)
- Adityavarman (870 to 895)
- Avasara II (895 to 920)
- Indraraja (920 to 945)
- Bhima (945 to 970)
- Avasara III (970 to 995)
- Rattaraja (995 to 1020)
[3]the third ruled what is now known as modern districts of Satara, Kolhapur and Belgaon between 940 to 1215 after which they were overwhelmed by the Chalukya.
Rulers
- Jatiga I (940 - 960)
- Naivarman (960 - 980)
- Chandra (980 - 1000)
- Jatiga II (1000 - 1020)
- Gonka (1020 - 1050)
- Guhala I
- Kirtiraja
- Chandraditya
- Marsimha (1050 - 1075)
- Guhala II (1075 - 1085)
- Bhoja I (1085 - 1100)
- Ballala (1100 - 1108)
- Gonka II
- Gandaraditya I (1108 - 1138)
- Vijayaditya I (1138 - 1175)
- Bhoja II (1175 - 1212)
The dynasty originally began as vassals of the Rashtrakuta dynasty which ruled the Deccan plateau between the 8th and 10th centuries.
Govinda II, a Rashtrakuta king, conferred the kingdom of North Konkan (modern districts of Thane, Mumbai and Raigad) on Kapardin (Sanskrit: Wearing the kaparda, a peculiar braid or knot of hair - also a term for Hindu god Shiva) I, founder of the Northern Silhara family, around 800.
Since then North Konkan came to be known
as - Kapardi-dvipa or Kavadidvipa.
The capital of this branch was Puri, now known as Rajapur in the Raigad District
Coin of Shilaharas of Northern Konkan , Billon, Dramma ?, Indo-Sassanian Design, circa 1210 - 1302.
Obv: Unrecognizable head of king. Rev: A horseman is seen sword-fighting against two foot-soldiers: a third appears to be attacking the horseman from behind, a fourth is seen dead at the feet of the horse
Obv: Unrecognizable head of king. Rev: A horseman is seen sword-fighting against two foot-soldiers: a third appears to be attacking the horseman from behind, a fourth is seen dead at the feet of the horse
The Silaharas of the Northern Konkan carried the Suvarna Garuda, t.e., the figure of a golden eagle, on their royal standard
A number of ancient monuments in Mumbai pay tribute to this dynasty's prowess:
and the Banganga Tank were built during the reign of Chittaraja, a king of this dynasty
The Ambarnath temple, also near Mumbai, was also built by Chittaraja in 1060
 |
| Ambernath Shiva Temple Picture |
The reign of the Silhara Dynasty ended in 1343
when the regions in and around Mumbai were captured by the rulers of erstwhile princely states of Gujarat.under
Raja Bhimdev
| सोलंकी Solanki Samrajya Solanki Empire | ||||
| ||||
| Capital | Patan | |||
| Language(s) | Gujarati | |||
| Religion | Hinduism Jainism | |||
| Government | Monarchy | |||
| King | ||||
| - 942/960-995/997 | Mulraj I | |||
| - 1143–1173 | Kumarpal | |||
| - 1242–1244 | Tribuvanpal | |||
| Historical era | Classical India | |||
| - Established | CE 942 | |||
| - Disestablished | CE 1244 | |||
THE LAST KING SAMANTSINH CHAWRA DID NOT HAVE ANY CHILDREN SO
HE ADOPTED HIS NEPHEW MULRAJ SOLANKI WHO OVERTHREW HIM IN
942 AND SET UP WHAT CAME TO BE KNOWN AS THE SOLANKI DYNASTY
SOLANKI DYNASTY:-
1.MULRAJA I 960/995 or 942/997 2.CHAMUNDARAJA | 3.VALLBARAJA | 4.DURLABHARAJA ----- Unknown 1009/1021 | 5.BHIMA DEV I | 1021/1063+ -------------------------- | |7.SIDHRAJA JAISINH 6.KARNA I [Karan Dev I] | 1063/1093 1093/1143+ | | 8.KUMARAPALA ----- Unknown (Brother) 1143/1173 | 9.AJAVAPALA | -------------------------------- | | 11.BHIMA DEV II (killed nephew) Unknown (die while Ajavpal was alive) | died 1242 | 12.TRIBUVANPAL 10.MULRAJA II 1242/1244
With the advent of Bhimdev and his followers begins the history of the growth and colonisation of Bombay.
The island of Mahim upon which he settled, had, previous to his arrival, been known as ' Mewale' or 'Baradbet' (the desert island); one of a group of isles, sparsely peopled by families of Koli fishermen and others, overgrown with babul trees, and dowered with a fine temple of Walkeshwar and a shrine of the ancient goddess Mumbadevi.
Here Bhimdev stayed and built a fair city of temples and palaces, for himself and his followers, which he called 'Mahikavati' (Mahim)
The island of Mahim upon which he settled, had, previous to his arrival, been known as ' Mewale' or 'Baradbet' (the desert island); one of a group of isles, sparsely peopled by families of Koli fishermen and others, overgrown with babul trees, and dowered with a fine temple of Walkeshwar and a shrine of the ancient goddess Mumbadevi.
Here Bhimdev stayed and built a fair city of temples and palaces, for himself and his followers, which he called 'Mahikavati' (Mahim)
DURING THE LATE 13TH CENTURY KING BHIMDEV OF YADAV DYNASTY ESTABLISHED HIS CONTROL AND CONSTRUCTED VARIOUS TEMPLES IN HE AREA.
|
Raja Bhimdev-2:-
was a 13th century king . He may have come from Anahilwada-Patan, Gujarat
Patan, an ancient fortified town, was founded in 745 AD by Vanraj Chavda, the most prominent king of the Chavda Kingdom. He named the city Anhilpur Patan or "Anhilwad Patan" after his close friend and Prime Minister Anhil shepherd. It is variously referred to in Sanskrit literature as Anahilpatak, Anahipattan, Anahilpur, Anahilvad Pattan
Qutb-ud-din Aybak sacked the city between 1200 and 1210, and it was destroyed by the Alladin Khilji in 1298.
Qutb-ud-din Aybak
| Patan | |
| city — | |
edwardes in his book The Rise of Bombay
has given the following account of Bimba :—
" Now the story of events subsequent to the victory of Alla-ud-din forms a most important portion of the history of our island. It is universally acknowledged that, after the defeat of Ramdev, a certain Bimba or Bhima Raja established himself as ruler of the North Konkan, and colonised the islands of Bombay : and our first duty is to try and discover the identity of a man who was the pioneer in the task of raising Bombay above the level of a mere fishing hamlet.
An old poem, the Bimbakhyan,
relates that king Bimbadev came to the Konkan by way of Anahilvada in the shaka year 1216, that is 1294 A.D., and halted upon the island of Mahim, which he found almost uninhabited. So charmed was he with the scenery of the island, that he caused a royal palace to be built there, and also houses for the accommodation of the royal guests and others, who had accompanied him to the Konkan through fear of the Muslim invaders of Devagiri and Anahilwada: with him there came from Paithan, Champaner and other places, 9 families of Yajurvedi Brahmins of the Madhyandin Shakha and 66 other families, that is to say, 27 Kulas or families of the Somavanshis, 12 of Suryavanshis, 9 of Sheshavanshis; 5 of Panchal, 7 of Kunbis or Agris, 1 family of Dasa Lad, 1 of Visa Lad, 1 of Moda, 1 of Dasa Moda and 1 of Visa Moda.
"Now some authorities, notably the late Dr. Gersonda Cunha, believe that the Bimbadev or Bimb Raja here mentioned was identical with one of the Bhima Rajas of the Chalukya (Solanki) dynasty, which reigned at Anahilvada in Gujarat; and Dr. da Cunha further observes in his Origin of Bombay that Bhim Raja of Gujarat after his defeat by Mahomed of Gazni at Somnathin the year A.D. 1024, " fled from his country, and, to make up for the loss in the north,marched with his colony from Patan into the south and settled at Mahim.
"But it is a well-known historical fact that, immediately after Mahomed of Gazni had departed with his army, Bhima Raja[Bimb dev-1] returned to his country of Anahilvada, and in virtue of his devotion to Somnath of Prabhasa, caused the temple of Somnath to be built of stones in lieu of the former wooden temple which Mahomed had destroyed, that he later sent an army against and subdued the chief of Abu, and that he reigned at Anahilvada till his death in the year A.D. 1064.
"Again, the authors of Prabandha Chintamani and Dvyashraya Jain chronicles of Gujarat have recorded the most minute details of the reigns of the Chalukya kings of Anahilvada and had the conquest and colonisation of Mahim or the Konkan by this Bhima Raja and his Gujarat followers actually taken place
,
It is indisputable that the Shilahara monarchs ruled these lands until A.D. 1260, and then yielded place, to the Yadavas of Devgiri.
according to old Marathi and Persian records, now in the possession of the family of the late Sirdesai of Malad, seized the North Konkan, made Mahi or Mahim (Bombay) the capital of his kingdom, and divided the country into 15 mahals or districts, comprising 1,624 villages ? "(S. M. Edwardes, Rise of Bombay : A Retrospect (Bombay, 1902), pp. 22-25)
Bimbashah, hearing of thedefeat of his father Ramadev of Devagiri by Alla-ud-din, fled with the Rajguru Purushottam Pant Kavle and eleven umraos by the shore of the sea, and took possession of the fort of Parner, and of Bardi, Sanjan, Daman, Shirgaon and other places. He thus obtained all the territory from Parner to Astagar. He came unto Mahi (Mahim in Bombay), and divided the country into 12 parts, giving the province of Malad and some villages from the province of Pahad unto the Rajguru Kavle. The Bimbakhyan also records that the king gave the village of Pahad to the Raj-purohit Kavle, and the village of Paspavli to the Senadhipati and Kulguru Gangadhar Pant Nayak.
" Lastly, a Danapatra, or grant of the rights of Sirdesai and Sirdeshpande, made by king Bimbdev to his Rajguru Purushottam Kavle in the Shaka year 1221 (A.D. 1299), shows that the province of the Konkan contained 14 parganas or districts, and 2 kashas or sub-districts, and that the island of Mahim (Bombay) was called a pargana containing 7 hamlets.
It further states that 'In the month of Magh Shaka 1220 (A.D. 1298) Maharajadhiraja Bimbshah purchased from Changunabai, widow of Govind Mitkari, the watan of Sirdesai and Sirdeshpande in the provinces of Malad, etc., for 24,000rayats, and after keeping it in his possession for one year and three months, presented it as a religious offering to his spiritual guide Purushottam Kavle of the Bharadvaja Gotra, on the occasion of a Solar Eclipse in the dark half of the monthVaishakh in the Shaka year 1221 (A.D. 1299), and in the presence of $n assembly consisting of the prime minister Madhavrao Shrinivas, Chitnavis Chandraban Prabhu, Patangrao Nyayadhish and others, merchants, mahajans and jamindars." (S. M. Edwardes, Rise of Bombay : A Retrospect (Bombay, 1902), pp. 25-27).
It further states that 'In the month of Magh Shaka 1220 (A.D. 1298) Maharajadhiraja Bimbshah purchased from Changunabai, widow of Govind Mitkari, the watan of Sirdesai and Sirdeshpande in the provinces of Malad, etc., for 24,000rayats, and after keeping it in his possession for one year and three months, presented it as a religious offering to his spiritual guide Purushottam Kavle of the Bharadvaja Gotra, on the occasion of a Solar Eclipse in the dark half of the monthVaishakh in the Shaka year 1221 (A.D. 1299), and in the presence of $n assembly consisting of the prime minister Madhavrao Shrinivas, Chitnavis Chandraban Prabhu, Patangrao Nyayadhish and others, merchants, mahajans and jamindars." (S. M. Edwardes, Rise of Bombay : A Retrospect (Bombay, 1902), pp. 25-27).
The above evidence leads us to the conclusion that King Bhimdev, who died in the Shaka year 1225 (A.D. 1303), was succeeded by his son Pratapbimba or Pratapshah, was none other than Bhima Raja, the second son of king Ramdev of Devagiri. It was a common custom among Hindu princes whenever they found their lives or Kingdom in danger, to send to a place of safety a scion of the royal house, in order that the vansha or royal line might not become extinct ; and it seems to us probable that Ramdev, seeing his other son Shankar overpowered, and being surrounded by the advancing army of Ala-ud-din, took the precaution of despatching his second son Bhimdev to the Konkan, which had upto that date been free from Muslim attack, and was indeed in the guardianship of Krishna, a viceroy of his own choosing.
With the advent of Bhimdev and his followers begins the history of the growth and colonisation of Bombay.
The island of Mahim upon which he settled, had, previous to his arrival, been known as ' Mewale' or 'Baradbet' (the desert island); one of a group of isles, sparsely peopled by families of Koli fishermen
The island of Mahim upon which he settled, had, previous to his arrival, been known as ' Mewale' or 'Baradbet' (the desert island); one of a group of isles, sparsely peopled by families of Koli fishermen
Bimb the misty king was the indisputable founder of Bombay;
and raised Bombay to the position of a capital under the title of Mahikavati or Mahim.
and raised Bombay to the position of a capital under the title of Mahikavati or Mahim.
These information from:-
in the village of Naigaon, which lies between Vadala and Parel, a spot known to the villagers as 'Bhima Raja's Wadi'. At present the place is occupied by the Arshe Mahal or Mirror Palace of Jivanlal Maharaj; but local tradition, prevalent among the descendants of Bhim Raja's followers, declares that here stood of old one of the two palaces, built by that king,
the principal seat of nyaya or justice. The second palace was at Kheda, Lower Mahim
In the Shaka year 1225 (A.D. 1303) King Bhimdev died, and was succeeded by his son Pratapbimba, as he is sometimes called. Nothing of importance is known or recorded of him, save that
he built another capital city at Marol in Salsette, which he named Pratappur. The name of the city still lives as Pardapur or Parjapur, a deserted village near the centre of Salsette.
"In the year 1318 A.D., after the reduction of Devagiri and the defeat and death of Harpaldev, son-in-law of the Yadava monarch Ramdev, Mubarak, the emperor of Delhi, ordered his garrisons to be extended to the sea, and occupied Mahim and Salsette.
But Muhammedan supremacy was probably not firmly established till later; for old Marathi records show that Pratapshah reigned for 28 years, that is, till A.D. 1331, when he was slain, and his kingdom usurped, by his brother-in-law Nagardev, the chief of Cheul.
"Nagardev reigned for 17 years, that is, till the year 1348, when his dominions passed into the hands of the Muslim rulers of Gujarat; and thus came to an end the sovereignty of old Hindu kings over the island of Bombay and its dependencies." ( S. M. Edwardes, Rise of Bombay : A Retrospect (Bombay, 1902), pp. 33-36.)
"Those well-known names 'Thakurvadi' and 'Bhoivadi' also date from this epoch; for the Thakurs, Bhoirs, and Gawands were three recognised divisions among the lower classes of Bhimdev's retinue. The Thakurs were the petty officers of his army; the Bhoirs or Bhois were his palanquin bearers; and both have left the legacy of their name of the locality in which they made their home.
| Seuna dynasty | |
| Official languages | Kannada, Marathi,Sanskrit |
| Capital | Devagiri |
| Government | Monarchy |
| Preceding state | Western Chalukyas |
| Succeeding state | Deccan Sultanates |
Raja Bhimdev was a 13th century king;and He is said to have built a palace and a court of justice in Prabhadevi and had his capital
Babulnath is an ancient Shiva temple in Mumbai, India. Shiva in the form of the Lord of the Babul tree is the main deity in this temple. The faithful climb up to the temple and obtain Darshan of the shivling and obtain blessings of the Lord. It is also possible to take an elevator up to the temple. The Bombay International School lies opposite the temple.
Babulnath Temple Shiva Linga and Idols were originally consecrated in the 12th century by the then Hindu king of the region. Over a period of time the temple was buried and lost over a period of time. The idols were re discovered (unearthed) in 1700 to 1780 time frame. The first temple was built in the 1780 year.
When rediscovered, 5 original idols were dug out. That of the main Shiva Linga, Ganesh, Hanuman, Parvati and one more. Out of this the first four are in the temple.
The deity in this temple is named after the Babul trees
which were the main components of a forest covering the low-lying areas of this island.
which were the main components of a forest covering the low-lying areas of this island.
During his reign he is supposed to have brought:-
Amongst Pathare Prabhu families 12 families belong to solar line and 17 to lunar line.According to the records[9] Pathare Prabhu rulers were at Ayodhya nd from there they went to Paithan and from there to Konkan. These records show that the people of this community eventually spread across the country.after the Turkic attacked and subdued the Pratihara rulers around the 12th and 13th centuries AD, some families migrated toMumbai and other regions in Maharashtra via Prabhas Pattan in Gujarat. Gentlmen from this community of Pathare Prabhu also held important position in the court of Yadava kings of Deogiri. After fall of Yadava dynasty at the hands of Alauddin Khilji; members of Pathare Prabhu community decided to return under the stewardship of King Bimba to Mumbai region along with their Yajurvedi Brahmins where other families had already settled
Palshis, Pachkalshis,
The Prabhus settled in the proximity of their temple of Prabhadevi, while the Somavanshis or Panchakalshis had their colony at' Parel. Here, they built three temples under the pa- tronage of the Raja, two for their family deities,* Wageshwari and Chandika, and the third for Mahadev, and called it Parali Vaijanath Mahadev. It is said that the ling of this Mahadev is Swayambhu or inar-tificial, and, therefore, it was considered of equal im- portance in sanctity, as the celebrated ling of Vaijanath at Parali, in the Dekkan. And as the Mahadev was called Vaijanath Mahadev, the village came to be called Parali or Paral .[modern name -parel]The temple of this Mahadev is, at present, situated in the middle of the Parel village, and is said to be on the same spot, where the old temple stoodBhandaris,:-Bhandari (Devanagari:भंडारी) caste is among the sea-faring warrior castes (Rajput) of ancient and medieval India. They migrated southward from Rajputana in early 1100 and subsequently spread over different parts of India. Along with Maharashtra, Goa, parts of Karnataka likeKarwar; they can be found in significant numbers in Nepal, Rajasthan, parts of Central India, Gujarat and Andhra Pradesh, Kumaon andGarhwal of Uttarakhand, India.Sheshwanshi Bhandaris arrived with King Bhimdev, who established his base in Mumbai in 13th Century
Bhois, :-in Maharastra, the Bhois were the palanquin bearers or doli carriers. There are altogether 22 sub-groups.the word ‘Bhoi’ is from the word bhovi meaning the leader or headman of group of vaddars community speaks vaddar language originated from Rayala seema meaning the land of rocks.
Agris:-The tradition common among them is that they originally dwelt at Mungi Paithan and were transported to the Konkan by Bimbaraja.The name Agri comes from Agar, a salt-pan
A studio portrait of a Kathiawar Rajput gentleman posed with a hookah, from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections. This was taken by Hurrichund Chintamon and shown in the Paris Exhibition of 1867
|
| Studio portrait of the Nimbalkar of Satara (a Maratha), taken at Mumbai by Hurrichund Chintamon c. 1867, from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections. This photograph was exhibited at the Paris Exhibition of 1867. A Maratha was a member of the princely and military class of the former Hindu kingdom of Maharashtra in central India (now the modern state of Maharashtra). |
| Portrait of three Parsees and a Parbhu, taken by Hurrichund Chintamon, c. 1867. As Europeans came into contact with other peoples there was an urge to document different races, customs, costumes and occupations.. |
| full-length portrait of two women and a child of the Vinchoorka family, Deccani Brahmins, taken by an unknown photographer at Mumbai, c. 1867. This photograph is from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections; one of a series of ethnographical photographs commissioned by the Government of India in the late 19th century to gather information about the people |
Parsees came later to Bombay when second english governor -Gerald Aungier requested 'all from every where in india ' to come and settle in bombay-
The Mughal Period:
The Muslim ruler Mubarak Khan of Khaliji dynasty
| Alauddin Ghilai (Gharzai),(Khilji), aka Ali Gurshap | |
|---|---|
| Sultan of the Khilji dynasty | |
of Gujaratcaptured the area from the Hindu rulers and established his dominance on the islands.
He appointed Maliq-us-Sharq as the governor of Mahim
and entrusted him the authority to make survey of existing rules in the islands and also amended the existing revenue system of the island. However, during the early
15th century the Bhandaris captured the island from the Mughal rulers and controlled the area for eight years.
After which the area was recaptured by Rai Qutb of Gujarat Sultanate.
Rai Qutb was an officer of the Gujarat Sultanate who had conquered Mahim, a village in Mumbai, India. During the early 15th century, theBhandaris seized the island of Mahim from the Sultanate and ruled it for eight years. It was reconquered by Rai Qutb of the Gujarat Sultanate. He died in 1429-1430
It is related that the daughter of the Rai of Mahim was given in marriage to Prince Fateh Khan, the son of Ahmad Shah of Gujarat.Ahmed Shah of Gujarat was a sultan of Gujarat's ruling Muzaffarid dynasty from 1411 until his death in 1442. Today, he is famously known as Ahmed Shah Badshah of Ahmedabad.
He founded Ahmedabad city and established it as the capital of the Gujarat Sultanate. The Ahmedabad city real name is Ahmed Aabad. The city Ahmedabad is named after its founder, Ahmad Shah.
After the death of Rai Qutb the area came
under the control of Ahmad Shah I Wali of BahmaniSultanate.
Sultan Ahmed Shah Al Wali Bahamani
After the decline of Ahmad Shah I the sultanate of Gujarat recaptured the area and established
during his dominance and constructed various mosques the major being the mosque of famous saint Haji Ali called as Haji Ali Dargah
The Haji Ali Dargah at Mahim built in 1431, in honour of the Muslim saint Haji Al
and Mahim daragah
However with the invasion by Portuguese the rule of Mughal emperors came to an end
.
The Portuguese in Mumbai:
 the Battle of Diu Changed World History ...
the Battle of Diu Changed World History ...
PAINTING OF ENGLISH SOLDIER AND CAMP
 ed
ed
the west coast for their establishments. Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat attacked Bombay and captured it. The Portuguese were becoming a force to be reckoned by 1560.
Chaul and Morro de Chaul Fort, India ...
The Portuguese arrived in India in 1498 and appropriat


Dutch Suratte - Wikipedia
The British in Bombay:
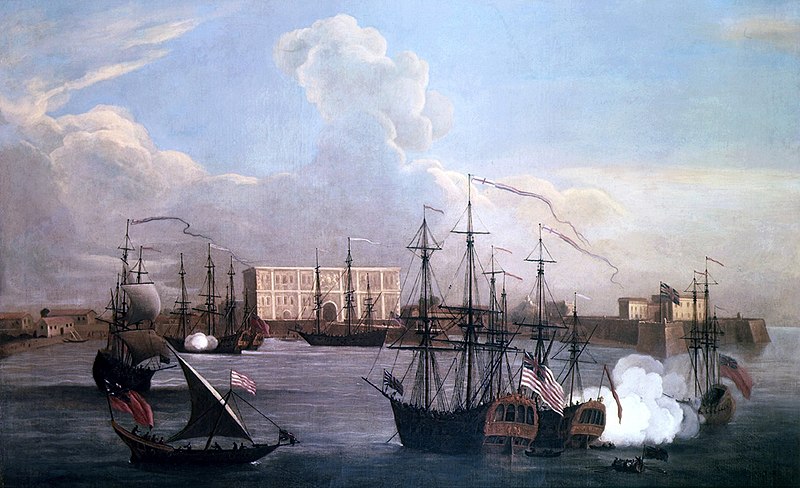
In 1661, King Charles II of England received ‘Bombay’ as port of the dowry and he married Princess Catherine de Braganza of Portugal. In 1668 it was handed over to the East India Company. East India Company shortly moved their main holdings from Surat to Bombay. George Oxenden was the first governor of Bombay.
The British built forts, huge custom houses and other buildings in the period, but the real development of the city began around 1857, the year of Sepoy Mutiny.
In 1858 by a special proclamation, the administration of the country itself was taken over by the queen of England, “Queen Victoria”, from the company. A Victoria wasappointed to rule the country in the name of the Queen. Politically Bombay came under the direct rule of British and this period marked the tremendous growth of Bombay.
| mahim fort |
Flor do Mar or Flor de la Mar (Flower of the Sea), spelled Frol de la Mar in all Portuguese chronicles of the 16th century, was a Portuguese nau (carrack) of 400 tons, which over nine years participated in decisive events in the Indian Ocean until her sinking in November 1511.
Out of service: 1511
Fate: Sunk in shipwreck
Sail plan: Full-rigged
Frol de la mar or Flor de la Mar (Flower of the Sea) was a Portuguese nau (carrack) of 400 tons, which over nine years participated in decisive events in the Indian Ocean until her sinking in 1512. There traveled Afonso de Albuquerque returning from the conquest of Malacca, with a huge booty and treasure to the Portuguese king, lost off the coast of Sumatra, making it one of the mythical lost treasures.
The battle ended in victory for the Portuguese, with the Gujarat-Mamluk-Calicut coalition all but defeated. The Mamluks
fought bravely to the very end, but were at a loss as to how to counter
a naval force, the like of which they had never seen before.
livehistoryindia.com
Battle of Diu (1509) - Wikipedia
| BANDRA PORTUGUESE FORT ;AT BANDRA,BOMBAY |
PAINTING OF ENGLISH SOLDIER AND CAMP
ENGLISH CAMP
Water-colour painting of a military encampment at the foot of a fortified hill by John Johnson (c.1769-1846). This image is from a sketch-book of 36 drawings depicting scenes chiefly in West India and Mysore, c. 1795-1801.
|
wdl.org |
the west coast for their establishments. Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat attacked Bombay and captured it. The Portuguese were becoming a force to be reckoned by 1560.
Chaul and Morro de Chaul Fort, India ...
colonialvoyage.com
The Portuguese arrived in India in 1498 and appropriat
vasai fort -before destruction
The Battle of Vasai was fought between the Marathas and the Portuguese rulers of Vasai, a village lying near Mumbai (Bombay) in the present-day state of Maharashtra, India. The Marathas were led by Chimaji Appa, a brother of Peshwa Baji Rao I. Maratha victory in this war was a major achievement of Baji Rao I's reign.
| CHHATRAPATI SHIVAJI SHAHAJI BHOSLE छत्रपती शिवाजी राजे भोसले |
[3]SAMBHAJI BHOSALE:-HTTP://EN.WIKIPEDIA.ORG/WIKI/SAMBHAJI
CHIMAJI APPA:-HTTP://EN.WIKIPEDIA.ORG/WIKI/CHIMNAJI_APPA
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

CHIMAJI APPA:-HTTP://EN.WIKIPEDIA.ORG/WIKI/CHIMNAJI_APPA
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Court of The Peshwas, Poona, 1790
View of the royal court of the young Peshwa Sawai Madhavrao of the Maratha Empire. Seen seated on a cushion concluding a Treaty with British official Sir Charles Warren Malet in 1790 in Durbar at Poona.
Painting by Thomas Daniell, 1805
Painting by Thomas Daniell, 1805
THE BRITISH AT SURAT FORT;BEFORE BOMBAY FORT WAS MADE
Dutch Suratte - Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org
| Dutch Factory at Surat 1634 (CAPTURED BY ENGLISH BEFORE SHIFTING TO BOMBAY FORT) |
In 1661, King Charles II of England received ‘Bombay’ as port of the dowry and he married Princess Catherine de Braganza of Portugal. In 1668 it was handed over to the East India Company. East India Company shortly moved their main holdings from Surat to Bombay. George Oxenden was the first governor of Bombay.
The British built forts, huge custom houses and other buildings in the period, but the real development of the city began around 1857, the year of Sepoy Mutiny.
In 1858 by a special proclamation, the administration of the country itself was taken over by the queen of England, “Queen Victoria”, from the company. A Victoria wasappointed to rule the country in the name of the Queen. Politically Bombay came under the direct rule of British and this period marked the tremendous growth of Bombay.
' The oldest known names for the city
are Kakamuchee and Galajunkja; these are sometimes still used. Ali Muhammad Khan, in the Mirat-i-Ahmedi (1507) referred to the city as Manbai. In 1508, Portuguese writer Gaspar Correia used the name Bombaim, in his Lendas da Índia ("Legends of India"). This name possibly originated as the Old Portuguese phrase bom baim, meaning "good little bay", and Bombaim is still commonly used in Portuguese. In 1516, Portuguese explorer Duarte Barbosa used the name Tana-Maiambu: Tana appears to refer to the adjoining town of Thane and Maiambu to Mumbadevi.

![Bombay Photo Images[ Mumbai]: BOMBAY FORT MAPS,PHOTOS,PAINTINGS,NEWS.1600 T0 1870](data:image/jpeg;base64,/9j/4AAQSkZJRgABAQAAAQABAAD/2wCEAAkGBxMTEhUSExIVFhUXGBgYGBYYGB0YGBgYFx0YFxoXFRcYHSggGBolHRcXITEhJSkrLi4uFx8zODMtNygtLisBCgoKDg0NFQ8PFSsZFR0rKy0tLS0rKy0tKystListLS0tLS0rLS0tNzctLTc3Ny0rKy0tLTctLS0tLSstLTctLf/AABEIAK8BIAMBIgACEQEDEQH/xAAbAAACAwEBAQAAAAAAAAAAAAADBAECBQAGB//EAEMQAAECAwQFCAgFBAEEAwAAAAECEQADIQQSMUEFUWFxkRMUIlKBkqGxFTJiwdHS4fAjQlNykwZDgqLiM1Rj8SQ0wv/EABcBAQEBAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABAgP/xAAeEQEAAgMAAwEBAAAAAAAAAAAAARECEjEhMlFBE//aAAwDAQACEQMRAD8A+szZpBYJftbX8Ig2j2TxEXWK9kCIqY4ZTLcQ42v2T4RPPB1VeHxiikxUJjNytQLzv2T2xHOj1Rx+kY0i0TnLpUReIcoIZPKBIOAfouaO+NM4FumukckQFXK3VdF1Mq92XSNVQcK25KhtC1Hqjj9I7nR6o4/SMORpKaUIJlKBJQFdBdAtKasdUxYcakqwah5NuXcBVLJWxKkpBDM4zqbykqZ2yfauSoavOj1Rx+kTzk9UcfpGWu1zCglMshQKgxCjggqBHRDi8AIJNnzCld1BCg928CyjRqAOx15YwuTw0TavZ8YjnXsnjGSm2TC/4ah0ks6FeqSmhpixNQaNhF0W5Yd5KziQGORCWe7m7jcXbGFyVDU517J4xxtXsnjCHLrIBuXfxLpoSQkEi8zDFhsAU8RNtSkm7ya1M/SAxYAvQUdyBtBwoIXP0qD/ADv2fGJFr9kxk84mXVkgg3SUdEvedbJYjYnjEqtMwiktQZaA7EuL4SogNhdcvRqHCFyVDU54OqfCO537J4iMqZb1hvwVMxJxxCQrq4OWctVJiOfqIvCWVBleqSoG7e1J9Z0M3tVrC5Khr869nxjjavZMZcu3FQmEJDpwDuTqLNQGra2MTMtKylTS1AgsM+tUBq4DJuljC5Khpc79k8Y7nfsnjCUieohjLKaVVXF1CgKa+qD/AJDGFJFrmiUCZajMKSSLqhdUEBTNdqCabyRVoXP08NfnfsnjE869k8YzpkyYJbsQrlAKJc3eUCXZuoXeOFpWWaWQbyQSQSLroc4DJSu7C5+lQ0BavZMW50NR8PjGYm1TCA0sg/h3nBwV6zBg5HvfJotNta0gjklLZ6gEOwfAA4mnZuBXJUHjaTkOMRzlWoeMZytIK6TSlEpyrXFn6NHAcbxHJt6yoJ5IsVFLlwKFVapwZBPakZwuTw0OdK1DxjhalahGau0TFLSkJUkXukpnoL4YUYPdB3LECs1umBKSpClEs/RKboIPsbMMqVrC5+nhr86VqHjEm1+yYyPSKzVMskXVOkOTe/DIBZPRLKVQ4s+EENsWWHJqHTAJYkNeSDlmCovldhclQ0+eeyeMdzv2fH6QNKhFkmFz9KgXl9n3wi8pb/e76wBZglkw+/vOLjM3STAxHS7PfAFZ74YbpdnvgKhU74mXSCNstZSoJCHcEu7YNsOuBi3K/THePyxe3WgIWHCj0TgHzEA9JS+oruxFW9IK/T/2PyxT0gr9Md4/LFTpNHUX3Ip6VQ/qL/jPwgGU2xX6f+x+WLC2q6n+x+WFvSSQR0F/xmLp0ol/UX3IBkWtR/IO9/xi6bSo/lHePywsNKo6i+4Yt6UR1JncMUNCYvqp7x+SLJWrqp7x+WFBpRPUmdwwT0gnqr7piA3Kq6o4n5YryyuqnvH5ICdIp6q+7C83SMtVDLmd0wDXOj1R3j8sRzw9Ud4/LGYlcgn/AKc3uqi5MnDk5ndVAOTLUSCChJBoQVUP+sdLtbUuAf5dr4YxnrVI/Rmd1XxiUTJB/sTO6fjANotISOjLA2A9uSdpiwt6uoO8flhEqkf9uvtBHxit+T/26+79IDU56W9Ud4/LHc9PVHe/4xnBUpv+gc/yK+MCmyZZqELG5B94ijW52rqjvH5Y7nauqnvH5IzEyZfVXn/b+kWTJQfyq/jHwgNPnSuqnvH5InnKuqnvH5IyxIS+Cv4osJI9r+LDxgNATSCTdQ5xN4ucq9CsCVai73EOzPeLtiz3MIRmWdJ6/wDF9YCbInWv+IfNAaYtiuqnvH5Ysm1qP5U98/LGTzVOtf8AH9YmXZU65n8f1gNWXOKQwQgAZBTeSNQiOeK6qe+fkhBNml61/wAcVTIRrmfxwGoJyiHATuv/APGF51vUkOUBmei6+IgFnkoS/SmHegfCInSkEH1+6G+giDcAglmNSN3kIoBESCyuHkIuPsTw4B0uz3xQip3wQY9kUOJhl1IIWuQFLYjINxMLK0ekZDu/SNE/9Q/tT5qgjRFYxsCdQ4D4RCdHJ6qeH0jZMQBAZA0enUnu/SLytHJ1J7v0jUiYDPFgRqHD6RUaPRqHd+kaRjnihLmKNXhFuaIOUNRwEQKqsqWoIrzRB+zDpEULwCQsct3bwgpsyGw8IYaJeAUNkRqigsSNsOkGIY/ZgE+ZJ2xbmadp4w0AYhlQARYU6jxPxjuYp1eJ+MMl4oxiiosqRlFhJTqi9dXjEjdADTISMhwieSTqHCLAmILwECSnqjhHcmNQ4RZzEEmAi4NQ4R1wavCJrEF4DuTGocIqJQ1DhEqJ1xAJ1iAnkxqEDtKBcVT8qvKCvA7WOgv9qvKAOEwIBlcIOkQIjpcIR7E8N/mG4+6KjExc4jcfdAxiYuXUgD+4f2p81QSB/wBw/tHmqDRlVDEiOUmOAiiXjoq8S8BLRxEc8QTAVJjgqJiBAWiDHRxiCscRHExzRRzxD7YtHNAQ8dXXEtHQFTviUmJKY4JgJiTENHNAREERZo54CscYmIMBUpjrkWIiICi5QJeOMvaYIqKwFQjafvsgNrkgoU5OB1aoZSIHa/UV+0+UA0mBJHTggisr1juHkIR7JPDBxG4+6KAVMXViNx90UzP3lFy6QCf+of2jzVFwYGpf4hHsjzMDtdq5MXiHGbY8DlGVMgRV4Tk6TlLJCVOxAyzAwDvnqyMOGKOjoqSWgE1cwVASdlQ+4/SAYMSYWl25B6wPVYv5VjplpVdcIL1xoNj0fwiA++LJjPlzicQTkahmOquyOnX3dIP2zAP90gHJ85KElSiwAqYoLUgh76e8IwdLzwVJTMoojokqZjrAFDQ8BABNoWv9H/yKN66ElqjO9/qYD0vLJ66eI+MWE5PWTxEedvVPrZj1jRipII1uQ/aN8CTPDBXTbBr2JCEzColsWJG8QHpxOT1hxEV50i+lF8XlAkJzIDu0eb5fNlEqTfuuKNyYaqTX8TwjCnW+aklYJCkKWEkVYEVADbGij6OtYFSQNsWEedkWpUywlS1Xl8mtRLXekLzMzClOEafpBDsFAFwLpxqQOAcOYB4xRUwaxFDMejg6/rWAmc2KabCBhvMAxyg1jjF4zLVaEFJF2v5XAD9JjdJ+6wKzzkXUnlDeNAxxYkVHZnAbDxBhBFqINDeBya6R/lhxgk61gEgpNB95wDcc0JielnYjMvjAE2pSVEOgjK8oA9hxPbxiDTaIaM1ekyFBwgpLjorBINGBBbbx4tg3mKTTZFByIqRCarSglSCzpbMVBGOO8dkRZ7RUhKgQCQxybFlZwD4gVpHQVuPlFTOU3qV3hvGBzZqiC6WFc/dAPxEjE7h5Rxi1nz7PIRcepPBVYjcfdFBnBCKjcfdFMzDLpDH0sqYJiSgP0QOJLZiMfSdrmXUKLUdQ23kKA/NnXhG5pQLvEy1XSEh9tTmx+zGIy53rupGDpq7BQrTIxlSsqWpctSroAWqWwx6r+4RsqtC5cu+t2JxCy7FiCKNr7IwrTaeTPJBBunF3o4TdZyWwHjlDCLVKEoS1hamZQJBL3nN2uF0EDFjXKANpG3TAOhM6RIDXklgSWGBOrjHT9JzUoKisukNRADkAVU+Dk44QJFrkKZxNxBuFOBG0HB3LA5xKuRWoOogXy7pKA11w5wxS3bAO2PSszkiVIvKegKmdJIxIBYhzRsIFaNLmipstYDlgm6pJajhRalcCBlDsqxSyxQUqGFDeGTuXLQpaLJKXK6agAlSyKtUEhmO77zBhM5C0/hrBJAOeH/5elIpOCr6DfWQXcAEhnFSK1YxazKQhki0UAACQxbBqsfsxafOYlpt4KQc3ALgH1fVocaNAJaQYMkUQosEkGt6jmrfmGXGAS7WKJSpgi+oNeAARRRSL9MW7eyAydIpMsBSiV1BZLqICbgL7s4r6SBXeCTeBfquBkoJcKG8cIBudPALqWSpZYetViU1N+laZ49kci3F0so4mW/SxF328KiEJ2kr8xHL9BL3klLpYghvWfbGxLtsoEETEGjAdBsRkBjQVgAItZa8FFlArFV1H4Yei8fxERlWWyFYmIVeIvEU2KTmdpTjr2GD6X0jNSoIkgEFySlAODABJZgOiKZEQ9oOzHk+itYKlBS9d5Jdtx8jFCtltqpczkBKKpaUkFLkFyMGGI369ldCVpWTMmlN1QUkgli4IIYkvRgTUmOtNnUidy/JKmKWpCSCHSlgwWKOlmDmFJWgrq1rZ0sbssJKbuYCSMWoOwQDx00kA9FL1wIJLH8t3FwOyBo0zeKSlBYqGq8xNRdFQQ7VYPujMkTEhV9YALhkVF17168auQWHZgIMqdLqCA2oLc+I8HgNWbaOUDhKnCmHQUfVNQ4S1SkZ57Ko6OtIXOnSglgFXqk0ZkNlXDdG1ooJ5MXXuuWd8y/vjB0dyaZs9S1BKuVWxKgOiWUKEti0BfSNuMrpXQwlksCXLqSKE1DC8fsRo+iFKYqWkh00u5BRKhjV0XE7Lr5wta+azLzzZZvBieUDt0aO9KpB+lIL6Rlsf/kDCn4o+P20BFssipaQpRvYBkpzdZUwKhilhsY64Ql6Slplsr17wxSQU3boP5jiUlQIOYzjWlTULPRmco1fWCgMA9PvGPI2y6Vqq5C1hmwAUQPsajsgN9c29LBIcqD3n6TXxTd0o5JlhICioesQAxpmb2WLaxSEtC2kEGVNKgj8rkgDOowaNS7IKgELDl2CVA8A2sQCc0KU12bcwNSUs9WLJL1yweHrNbgoLvFCgCNQDHKrbuyDTbOmgug9g2/CPOyZQSo0DhRphSreDQG7o6eiYZl4ACpFSBda4ScsE47YtMnylKASVKINNQrWuY4xlos5ZsMddXL4b4bsFkIW7lqYjGo2QHpFQSzZ9nkIGRBLPhw8hGsepPBlYjcfdA2qfvKLnEbj7opmfvKJkQWnteVewupej5qyjOm6RlANLZZLnoh0u2ZSW4Q5bbNyiim8QLqXYs9V4x1l0bLRgPKMq8/M0Sueu+tN0UDdIO3iYam6JlSwlklytI1cA8bs1QA+/tow7fbJRMs8qiq0/nFEsTeNaOa7KQD8uzyh+RNMXy45RmyTLWlboDXipJZqIUP8Aif8AIbYaNoM0tLMtaUsVfiY5sWSaYHaDClkMxSClIl3ioqDklrzhy2Rchsw+VQB1SZaSVKQut4XLl5LgliFAP4kQoZkuWi7yKlKU9LrY41VTFy8bmjRdTXNa3O28cd/wEOEwGLLWhldCWCQyQhyQ74qIAOWA7YR/qTRwVKTyaChlpLncqjAk4kcNkemeM3Sy19EAJu4kmpcbMM4DyMuwoJTeUUlqkpOoMEtt8o07IiQFeskh2BBuUYVdTZvQEnZWM6eouQasVbHZxlujpcxwz0JA8fjBXs5FglsCKg1d3fbti82zy0gquJpszg8iWEpCUgAAMAIU0iSQoAEskswJdSgwwGQJ4iKgejrOyGWkOMDSrh8NYdoix2dClKUUpIJN2mpgTxHhFLRpeWlYlELJJNABQEs5cghn8ICvSAlFKEpvnpkBKgXdRZKQHLsrNhQxBqLsEpWMtJ3gQMWGUlyZaWo3RG5hDBnpBulQB1PlAbWi8HEwpugl0lLYZ3gRljtOuKMwykqTIIQgEm8oXX6LEnVV2FdsOSbBJUrlEgUdJAHROGXvEISpYuIUJiyVnompZtktgzAnKH9Gq9ZlJUm8sFslA5scTjEGfbf6eCphUA761HwcwTRGhLhmX0pIJBTngG7I2pswJBVkK0xgaLbLKgm8HVgMzR/KKKejpX6aeEX5lL6ieEFVNAIBIc4B6nOgiZii1MdtB2ljALmVLUo0BKCz4M4B+EAsdmlgqZCfXNcS9MScavCwUozJiXShym+oLDgXRRLoxwqde6Ayp6iopCpigld24AgOEjpOSEi6CGpR23QGtIlpIe6iuBFXDCp1Zhqxy7Eg6x+0lPkYX0XaXShLEC64Ju5MDS87V1RoPAJq0cj/AMn8sz5oyE6K6ZWiiCQXV0irAUCiabTwMbdptBSAQL2sOx7NuykIrt5YAJIO1KjhsSmAal2GWlLFIpUkhycySYuuQkCiRRm4iMa1aVnlYTLlm67ElCwz7wCewRrIPQIrjmCKFVMdjQDhEXs+HDyEVMXkYH7yEXH2SeLqPSG4+6KgVMXXiNx90UTnDIgH+4r9qPNcXBij9NX7U+a4iclwQ5G0YiIofLAL6RalN2fbTwjE/qC3JPJiWtAN93JAFA959QAxZqiCTreDNS8wBNHLM/rteBwNR51DgGtsqX+DcCbpW7gCtD8Ygoq1IV05ZcJAC0JUCVJLMxCqqBNK1c6wYFoayyuTUVpSoOSSrpBklQFTiwGMaK5gZS36KHI3gVV7u07IwrPOWkMGIJvKfBFSQTmUlRGGo5EsDNksSC4CUg31FTpQbiQo0HR9Y3WfY+QjXsE9xdNFJABD4jI+7eDGEdJiVLUkdK9eJOJckY7SkkjsyhiQk84lTm6MwLTeDVoVIvNrSniBugNm0WoIBKgWAegfg0IWi0hZDuAAo1SpNKOXUBswjWugwhabJKKVLMtLlKsQHLAvvNHgPIWm0A3ljB36Ooq+Fe0QpzkMAAxoRvfxqI17bYkuaCtcPADjGTbZYJDEUehGDNlqxgr3ejrQmakKYVD1Yli/vB7AIaVIScUg9keZ/paff5IAEcmiagtgohSCX3Xhjn2v6OQSCQT2ZwRcWdGNxL62EcbMg4oSewQUR0AuUy0EC4kO7MA5IDsOx+EBtFp9ZISpQIxTdDAgU6RGZ8TFNJHpILOUlJ3OpALdlO2KW67LUFksFOkh86KB/wBW7d8BmpkFTBRmAIDs6AAbt5g1fVZidZjpNhCQLqlFQUo9Jag6SoOOgoM5fEM8Vt88gOhQogO3TcgLcAJwHSAc4NGdL0goLSlS0m9dCkuoE3iFEAXaV1F6Z5h66zlK0hd0VxcChFPN4MmSjqp4CA2GXdCk4AKLZ0PSxO0mGCYDky09UUwoIDaJoRgHUcAB40yggJ+zCGkrCV1QpSVUdlEBQGShhrrtOMAmkKckh1k3koOAVQiZM/aMhhQByxgdkQpIuoHSWQpa1HJTZCpJJLBxmXxgyLPPJcoS5ABN/EDckeUAnWCeQQlEmvWmKUMGe6Zfvig+jlJlgAKSVC4ldXIvKugFvVAyFBxjajy39P6KUgzQprzFJKSyEhVSzipJAw6o1xs2i0TwBcQglxeJPG6KecBoqioEDStRD3WOpx7olKjmk8RAGaAzxTtHmIJA52HanzEAeLyMD2eQgZi9nw4eQi49SeCK9Ybj7oqkVMSfW7PeI4ZwyIAHrq/anzXEqUM4XnTgJhBLdFJ8V/SOUQc38fOMqtaUlSVAM7FnqCWo43x5K3aRnGYEkgXSWBJvCjMc1bDqYucY37Ro+Stitjqw92MLTNGSC9WLCoVkN5YdjQGDbdKzWUkSwkKCQpSQo4UHsigbcIzJlvUQVKUBiakCpxa7hh4R6saNksAVXgMiXfsgXoCRiHGxKmbinCA8qmWu0XUS0lZzN28A+d5VWpsxj39lsqpcuVLSaoKXJdmd1APVmcB9kY50TyZ5WSshQ1nHYo5jfG2q1pqARtDP5QB51sSkspw2bFtbO2OyMzTlsRcQxe+SxBY3WuqYioPSAfbDiEyVAvLScj0H4uIxf6h0ckISqWhIuu4DJcKbB2FLop/6gJNpQU1JFDUglVBRyAzn4mMm2WqWolCEqxYKIDgFnNfpjsgQnOksiZtar6xhvgSpispSnwvXaEYVDM7FqcItD0/9KyEJlhSVLNCC7XSXqMMmTnWHTaguYi694EuPZDu/ANvjH0Zb5iZV1Mt3USzEgAtRxQmhJrn2Q7ZLXMT/AGEucTeYneanwiK3RN2RBmnUPHyhUWnouboOq9TsJSIgzz1f9m90EZemUTwE3JrKUoJfEkEjWC1QNZg+l+WCUEKSlQo7BQVTMEC6aYjhDyiFM4BYuKqLHLLGLKCSoE4pyfXvEFYhsVtU96agBsAks2Llk47tQhex6NN9N5yxCmcpSTRnQVF6sduyPQkoc697v2H4RSZLluDebZhCwKfInkkifd1AIDdhJ84PKVOzMvgo9uMX5dON6m8/GB88l5K1Z/WCClUzWjgfmiyFKzKewH4wDlpfWx9r3ExdRTrDHLA8b3ugDTpyUh1EAYPtMVRaklyFAgYl6DthKdKlqT69Dj0i/YQaHdC0yxyTi9da1qPElxAaQ0hLJAvByQBk5OAGs0PCGQqPPy9FyAq9V65l66nJIFWpkd0ENlk61dq1/NAbhXEpVGTJSgChI2uX8SXgkiclJ9dRJyU3hQQGoowKdh2p8xCxtY2eHxiF2gbMU8XTQxRoGL2c+QgJMFsuHYn3wx9knghPT7PeIqk1MT+c7oq9TDLpDC/qOYUm8B+UB9ZdVNkYCtKqGKjvo3AlzHtrVYpcxr6EqbC8HbdCx0RI/RR3R5xFeI9LKJ9YjcBETNIKFSvHXiOPnHtzoSQf7KOEVGhLP+ijtD+cUeFGkDeHTrkw+Ii0vSS3Lr2ZEUxfpCPb+hbN+hK29ARX0LZxUSUdg8og8cNJKApM/wAaB9xcxHpI7fCnbHskaIs7/wD101zKQ3bBVaGs9fwJfdGPCA8fK0qsAErPY3jUNA5mkL1Sz6yflVHthoez/oSu4nwpHHREj9CUNyAPdFHiOVB9XgFXu0UMBVOIo5z9Z9m8x7tWhrP+hL7ojkaMkj1ZSB/iN0QePs1uUjopbxNdbXQeyCq03MFSsDa1Nz5GPUHQ0jOTL7oMcnQtnBfkJfdHwgryczTyxitnrRNfFOEHRppeJncUgeH/AKj0x0PZ/wBGX3YodB2f9FHAjyh4HmfTUx2v68hXgYhOmVlxyhJ2Mfew4R6f0FZ/0U8DHHQFm/RT4/GHhHmpelZicV49YM3hEzNJrOCh2Y+fuj0g0BZv0U+PxjjoCzH+ynx+MPA8zN0ocM9tPf8AGAek5gxfdT3R60aAs4LiUBuKh7470DZ/0/8AZfxi+B5RGlFgu5YnV9awRWmFkDHHGjHsr5x6n0DZ/wBIb3U/nEegLOMJTblKHvgPInTE12vU1l23YtEHSqxq4P2Y/GPWnQMh35Ov7lH3xx0DZ/0hxV8YDyB0ocq+A7IpM0io1qRqd/fXwj2XoGz/AKQ4qPmYj0BZ/wBIcT8YDyaNIqDVUnUwP1Ecq3l+hezq5L76huEeqOgLN+iG7fjEJ/p+zDCSnx+MPA8v6QmGnSbIjZvVXwgkm0rvoBX+dFCQaXk6iTHphoKz/ojx83giNDyAQRJQ4LgtmGY1gHFGDWT3J98BVBrGPJPvhj7JPFx6xPZFSBr8YZiLg1CNTjZZbonBXjHEbTB1SUnIRQ2VOptxialhiuuJ5PaYsLLqJ4v5xJkHX4RNVtRUvfC02ahPrrbVWvBoZVJVr4Rm2rQEuYoqWVl8ReIHhEnGfxYmP0tM09JSu4VHFgqhB+kXRpuzkPyzB2rvbVBrN/TkiX6ssdvSPFTwaXoCzg3uQlvruD4RP5yu0CySlQdMy8MHBBHEQQSvbPEfCCSbEhIZKQBqAbygokJ1CNfzTYsZA6x4j4RxlpGKiH1kQ3ySdQjhKGoRdE2KCSNZ4x3IDWeMOCUNQjuTGqGkGxPkE4OeMTzcazxhxKAMokpEXSE2knyA1njHCSNZ4w3cGoR10ahDSDaShljWeMcbuavGG7o1CIVLGqGkFlUoBwJjuT2mGggDL3xLDVDSCyl3aY4p2mG7o1CIKBqEXSCynJjbFbm/fDoljUOEVMpPVHCJoWWKPa8Yqz4Etry+sOCWNQihkJ6ohoWWCDmXgKphwS511AZ9bw/zdPVHCJElPVHCGhZBKTmrh8YIkA4End8YbEsahwi0NILKCyvi47XMMS5QThF4iNRjEJcv/9k=) BOMBAY FORT MAPS,PHOTOS,PAINTINGS,NEWS ...
BOMBAY FORT MAPS,PHOTOS,PAINTINGS,NEWS ...
BAMBAIM(BOMBAY)
'BONBAS' TOWN- ( MAP OF 16TH CENTURY BOMBAY )AND FORT 'BOMBAIE'


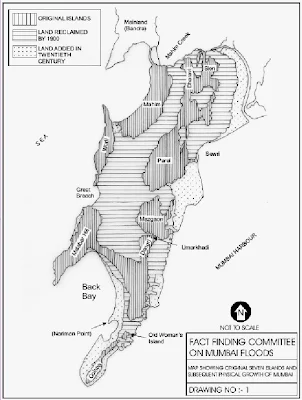
THESE 7 ISLANDS WERE JOINED TOGETHER TO FORM THE BOMBAY ISLAND:-
The inroads of the sea at Worli, Mahim, and Mahalaxmi turned the ground between the islands into swamps making Bombay an extremely unhealthy place at that time due to prevalence of Malaria. Many commuters going to the Fort by boat between islands lost their lives when there was a storm during the monsoon season. During the next 40 years much was done to improve matters. Reclamation work to stop the breeches at Mahalaxmi and Worli were undertaken. The work on the Hornby Vellard began in 1708 during the Governorship of Mr. William Hornby (1771 to 1784). The directors of the East India Co. objected to the expense of its construction, but Hornby did not give orders to stop the work and it was completed in 1784. In 1803 Bombay was connected with Salsette by a causeway at Sion (1803). The island of Colaba was joined to Bombay in 1838 by a causeway now called Colaba Causeway.
.


are Kakamuchee and Galajunkja; these are sometimes still used. Ali Muhammad Khan, in the Mirat-i-Ahmedi (1507) referred to the city as Manbai. In 1508, Portuguese writer Gaspar Correia used the name Bombaim, in his Lendas da Índia ("Legends of India"). This name possibly originated as the Old Portuguese phrase bom baim, meaning "good little bay", and Bombaim is still commonly used in Portuguese. In 1516, Portuguese explorer Duarte Barbosa used the name Tana-Maiambu: Tana appears to refer to the adjoining town of Thane and Maiambu to Mumbadevi.
Gerald Aungier
Gerald Aungier was the second Governor of Bombay. He was made the president of the Surat factor and the governor of Bombay in 1672, which posts he held till 1675. He was responsible for the initial growth of the city. He died in the year 1677.Although the Portuguese king had ceded all the islands of Bombay to the British king Charles, the Portuguese in India refused to hand over the the territory. It was not till 1675 that Aungier actually took possession of Colaba and Old Man's Island, thus completing the transfer of power to the British. His plan of fortifying the main island, from Dongri in the north to the harbour, had to wait until 1715 for completion, when Charles Boone became the governor of the town.
ALL WELCOME,FROM ANY ANY PLACE IN INDIA TO BOMBAY SAID AUNGIERlHe offered various inducements to skilled workers and traders to set up business in Bombay. His offers were tempting enough to lure many traders and artisans from Gujarat to the newly developing town. As a result Bombay registered its first population boom. Between 1661 and 1675 there was a six-fold increase in population.
ded land near the Malabar hill to immigrant Parsiworkers and traders for a Tower of Silence.
It was during his governorship, in 1670, that the first printing press was imported and set up in Bombay.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bhimjee_Parikh
[Bhimji Parikh (b.?-1686) was a bania born in Surat. He is remembered today primarily for having introduced the firstprinting press,[2] to Bombay in 1674-75.]
n Bombay, Governor Aungier formed a militia of local Bhandari youth to deal with organized street-level gangs that robbed sailors in 1669. Thus, Bhandari Militia was the first police establishment in Mumbai(then Bombay) during British India.
[Bhimji Parikh (b.?-1686) was a bania born in Surat. He is remembered today primarily for having introduced the firstprinting press,[2] to Bombay in 1674-75.]
A GROUP OF 8 PEOPLE DRESSED IN SAGGY YELLOW PANTS AND BLUE PARSI TYPE CAPS MAY BE THE BHANDARI MILITIA (BOMBAY'S FIRST POLICE FORCE UNDER BRITISH);WITH 2 SENIOR OFFICERS?IN BLUE BOTTOMS AND BLUE CAP
.BUT ACCORDING TO ONE HISTORY BOOK WRITTEN LATER ; BHANDARI MILITA HAD BLUE PANTS AND YELLOW CAPS oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com
BAMBAIM(BOMBAY)
| BAMBAIM(BOMBAY)MUMBAI-portugese map 1630 |
'BONBAS' TOWN- ( MAP OF 16TH CENTURY BOMBAY )AND FORT 'BOMBAIE'
| FORT DE BOMBAIE(BOMBAY) |
| MAP SHOWS FORTS AT BANDURA(BANDRA) MAYEN(MAHIM)MAZEGOEM(MAZGAON);CAYMAN(SION)AND BOMBAY FORT |
| BACAIM(VASAI) FORT AND BOMBAY FORT SEEN IN MAP READ -CAPTAIN KIDD THE PIRATE IN BOMBAY BEFORE HE WAS CAUGHT IN NEWYORK:-http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2009/02/kidd-pirate.html |
| MAP OF BOMBAY BY FRENCH NAVIGATORS |
| MAP OF CAMBAY SHOWING BOMBAIM(BOMBAY) AND MAIM(MAHIM) |
1670--View of Bombay (East India men flying Company’s Ensigns). - by Edward http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010/12/1670-view-of-bombay-east-india-men.htmlhttp://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010/12/1670-view-of-bombay-east-india-men.html
The british Fort, Bombay, Harbour face wall,-GUNS POINTING DOWN INTOMOAT 1863.--Date: 1863--Photogrph |
The inroads of the sea at Worli, Mahim, and Mahalaxmi turned the ground between the islands into swamps making Bombay an extremely unhealthy place at that time due to prevalence of Malaria. Many commuters going to the Fort by boat between islands lost their lives when there was a storm during the monsoon season. During the next 40 years much was done to improve matters. Reclamation work to stop the breeches at Mahalaxmi and Worli were undertaken. The work on the Hornby Vellard began in 1708 during the Governorship of Mr. William Hornby (1771 to 1784). The directors of the East India Co. objected to the expense of its construction, but Hornby did not give orders to stop the work and it was completed in 1784. In 1803 Bombay was connected with Salsette by a causeway at Sion (1803). The island of Colaba was joined to Bombay in 1838 by a causeway now called Colaba Causeway.
.


THE PORTUGUESE , GAVE BOMBAY(FORT AND SURROUNDING AREA) AS DOWRY OF THEIR PRINCESS; TO CHARLES 2 OF ENGLAND}in 1661, Catherine of Braganza
as part of her marriage dowry.
| The statue of Robert Clive (1725-1774) on Horse Guards Parade in London |
 |
| DURING THIS PERIOD THE BRITISH FLAG WAS FLYING OVER BOMBAY AND AMERICA |
 |
| BOMBAY FORT- GUNS ARSENAL |
| Former type | Public |
|---|---|
| Industry | International trade |
| Founded | 1600 |
| Defunct | 1 January 1874 |
| Headquarters | London, United Kingdom |
The East Indiaman Repulse (1820) | |
| Colonial India | |
|---|---|
| Portuguese India | 1510–1961 |
| Dutch India | 1605–1825 |
| Danish India | 1620–1869 |
| French India | 1759–1954 |
| British India 1613–1947 | |
| East India Company | 1612–1757 |
| Company rule in India | 1757–1857 |
| British Raj | 1858–1947 |
| British rule in Burma | 1824–1867 |
| Princely states | 1765–1947 |
| Partition of India | |
VIEW OF SOUTH BOMBAY 1820 -MAZGAON AREA |
Lithograph of Bombay harbour by W. Watson after Charles Franklin Head from his 'Eastern and Egyptian Scenery' printed by C.Hullmandel and published in London in 1833
A GROUP OF 8 PEOPLE DRESSED IN SAGGY YELLOW PANTS AND BLUE PARSI TYPE CAPS MAY BE THE BHANDARI MILITIA (BOMBAY'S FIRST POLICE FORCE UNDER BRITISH);WITH 2 SENIOR OFFICERS?IN BLUE BOTTOMS AND BLUE CAP
.BUT ACCORDING TO ONE HISTORY BOOK WRITTEN LATER ; BHANDARI MILITA HAD BLUE PANTS AND YELLOW CAPS |
The Hornby Vellard was a project to build a causeway uniting all seven islands of Bombay into a single island with a deep natural harbour. The project was started by the governor William Hornby in 1782 and all islands were linked by 1838. The word vellard appears to be a local corruption of the Portuguese word vallado meaning fence or embankment.[1]
It was completed in 1784 and was one of the first major civil engineering projects which transformed the original seven islands of Bombay into one island. Work on the vellard was started in 1782 by William Hornby, then Governor of Bombay, against the wishes of the directors of theEast India Company.
The purpose of this vellard was to block the Worli creek and prevent the low-lying areas of Bombay from being flooded at high tide. The cost was estimated at about Rs. 100,000.
According to some accounts, Hornby ordered the work to be started after the East India Company turned down his proposal; and continued as Governor till the end of his term in 1784, ignoring the suspension notice sent to him.
One story of the origin of the Mahalaxmi temple links it to a vision of a statue of Laxmi in the sea. The chief engineer dreamed of the statue following multiple collapses of the sea-wall; recovered it, and built the temple as an offering for safe construction of the vellard.
|
BOMBAY ENGLISH COIN 1770 -15 RUPEES
| This photograph of the city of Pune was taken by an unknown photographer in the 1860s to from part of an album entitled 'Photographs of India and Overland Route'. Pune was the eighteenth-century capital of Raja Shivaji, the Maratha king who defied the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. In 1802 Jaswant Rao Holkar defeated the combined armies of the Peshwa and Scindia. As a result of this defeat the Peshwa invited British assistance and Pune was occupied by troops under Wellesley in 1803. After the battle of Kirkee in November 1817 it was surrendered to the British who based the summer headquarters of the Government of Bombay here and established a large military cantonment. |
| POOR MAN'S PALANQUIN below-Post haste-PIGEON POST-[email of last century] |
| POst men running with postal articles 1850's picture[ called dawk wallah by english men ;Scinde Dawk was a very old postal system of runners that served the Sindh, The term also refers to the first postage stamps in india the forerunners of the adhesive stamps used throughout India] Darius extended the network of roads across the Persian empire, to enable both troops and information to move with startling speed. At the centre of the system is the royal road from Susa to Sardis, a distance of some 2000 miles (3200 km). At intervals of a day's ride there are posting stations, where new men and fresh horses will be available at any moment to carry a document on through the next day's journey.By this method a message can travel the full distance of the road in ten days, at a speed of about 200 miles a day.other methods of communications in the past were [1]'message whistling' of canary islands[2] 'tom tom' messages by drum beats,[3]fire signal by south american indians[4] smoke signals by north american indians
Read more:http://www.historyworld.net/wrldhis/PlainTextHistories.asp?historyid=aa93#ixzz1I3DbRsDn Read more:http://www.historyworld.net/wrldhis/PlainTextHistories.asp?historyid=aa93#ixzz1I3DOcxXC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| India postage 1930 - SHOWS THE 'Dak runner' |

late four from J M Gonsalves' 'Views at Bombay'. During the 1820s, institutions for currency production were constructed in various parts of India including Bombay, Benares and Calcutta. These imposing Doric structures can be seen to represent the feeling of growing political power of the English. The Bombay Mint was constructed between 1821and 1829 on the site of the Fort rubbish dump. The architect was John Hawkins of the Bombay Engineers. The building on the right of the picture is the Town Hall.
icture of six 'Native Judges and Officers of the Court of the Recorder, at Bombay', at the beginning of F W Blagdon's book, 'A Brief History of Ancient and Modern India'. According to Blagdon, these drawings 'were taken from life in 1758' and are labelled respectively as holding the following positions. '1. Judge of the Hindoo Law, Antoba Crustnagee Pundit. 2. Interpreter, Rhowangee Sewagee. 3. Hindoo Officer, Lellather Chatta Bhutt. 4. Judge of the Mohomedan Law, Cajee Husson. 5. Officer to the Mooremen, Mahmoud Ackram of the Codjee order or priesthood of the cast of Moormens. 6. Haveldar, or summoning Officer, Mahmound Ismael'.
1838.
Engraving of the Grant Medical College showing part of Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy's Hospital in Bombay by G. R. Sargent from his own drawing and published by him in London in 1844. The engraving was printed by M & N Hanhart. The Grant Medical College and the Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy Hospital were built in the 1840s and funded jointly by Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and the East India Company. Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy (1783-1859) was a Parsi merchant and eminent philanthropist. The Grant Medical College is shown in the foreground of this view. It was named after Sir Robert Grant, the Governor of Bombay between 1835 and 1838.
The idea for the construction of a wet docks for the use of shipping in Bombay harbour was first suggested by M. Malet when member of Council in 1855. In 1866, Russell Aitken, Executive Engineer to the Municipality prepared the foundation of a Harbour and Dock Trust which could raise money for the construction of wet docks on the Elphinstone and Mody Bay reclamations as private companies had gone into a recession. In 1875, the first stone was laid in the hope that the new dock would create a prosperous revolution in the trade of Bombay. In April 1879, the Prince's Dock was thrown open by the Governor of Bombay, Sir Richard Temple. In 1884, it was decided to extend the dock and construction then began on the Victoria Dock.
Photograph of a group of pupils from the Juggunath Shankarset Girls' School at Bombay in Maharashtra from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections: India Office Series (Volume 46), taken by an unknown photographer in c. 1873. This image of pupils posed on the verandah was probably shown at the Vienna Exhibition of that year. On the photograph, there is a letterpress caption, above the main caption, which reads "Student's Literary & Scientific Society, founded 1848. President Dr Bhau Daji." S.M. Edwardes wrote in The Gazetteer of Bombay City and Island (3 vols, Bombay (1909-10), "...The Students' Literary and Scientific Society, which supported nine vernacular free schools for girls, attended by 654 pupils, of whom 136 were Marathi-speaking Hindus, 120 Gujarati Hindus and 398 Parsis...The formation of this society was promoted by Professor Patton of the Elphinstone College in 1848. It was intended by the student and assistant teachers of the Elphinstone Institution to be a mutual improvement society and to aid the dissemination of knowledge by means of vernacular lectures and the publication of cheap periodicals in the vernacular languages..
also see -A photograph of a view of Bombay from Malabar Hill from the 'Vibart Collection of Views in South India' taken by an unknown photographer about 1855
ALSO photos of bombay http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010_07_04_archive.html
Glimpses of old Bombay

and ran off over the hill
BELOW VIEW OF BOMBAY 1854--
[3]BELOW THE OLD BYCULLA RAILWAY STATION
ALSO photos of bombay http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010_07_04_archive.html
| VIEW BOMBAY FROM MALABAR HILL 1850'S |
BOMBAY HOTELS 1850'S http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2009/02/bombay-1800-1900-bombay-hotels.html
BELOW ANOTHER VIEW OF BOMBAY FORT AND HARBOR
TRAVEL BY SHIP:- http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/02/travel-by-ship-before-1960-bombay-to.html
| The Fleet under Convoy of H. M.'s Ship 'Chiffone' Captain Wainwright leaving Bombay'. Coloured aquatint by J. Clark after Robert Temple. H.M. 65th Reg. Sept. 14, 1809. From the Apollo Gate[COLABA ISLAND SEEN IN FRONT OF HARBOR] |
MAHIM CHURCH AND MITHI RIVER (before people converted the river into a sewer)
THERE WAS A deep gulf-SEA- between Mahim and Sion
|
Glimpses of old Bombay 
THE WILD BEASTS OF BOMBAY. /TIGER AT MAHIM,HYENA AT BYCULLA,TIGER AT ESPLANADE,TIGER AT MAZGAON,HYENA AT MALABAR HILL,TIGER AT GOWALIA TANK
THE WILD BEASTS OF BOMBAY.
1783. — The Governor and most of the gentlemen of Bombay
go annually on a party of pleasure to Salsette" to hunt the wild
boar and royal tiger, both of which we found here in great
plenty. — Hector Macneill.
1806, December 17th. — Two gentlemen at 7 a.m. riding
towards the bungalows of General Macpherson on the Island of
Salsette, near the village of Coorla, two tigers came out of the
jungle as if ready to spring, crouched, and were observed to
betake themselves to the jungles and hills of Powee, fifty yards
in front of the horses.
And in this connection two persons on November 4th
were carried off by two tigers from a native village nearly
opposite to Powee, near the high road leading from Sion to
Tanna. The natives believe the tigers are human beings, and
have gold rings in their ears and noses.
One native's body they had sucked all the blood out of it,
otherwise not eaten. They took away a herdsman driving
his fl^ck.
1819, — There were in all only three deaths recorded in
India of Europeans from snake-bites in the years 1817, 1818
and 1819.
1820, December 23rd. — A large lion killed within eight coss
from Ahmedabad.
1822, February 9th. — A tiger on Malabar Hill came down,
quenched his thirst at Gowalla Tank,
 |
| Gowalia tank at Malabar hill |
between the Hermitage and Prospect Lodge. Prints of its feet
were distinctly visible this morning.
1828. — At Colaba Ferry a huge shark was observed in
proximity to some bathers.
1830, January 13th. — A large hyena is prowling about
Malabar Hill on the western side between Mr. Nicol's residence
and Vaucluse, " as good sport as a Mazagon tiger." — Bombay
Gazette.
1839, June 25th. — Lieutenant Montague, at Colaba, returning
from mess, put his foot in a hole, received a slight wound which
in twenty-five minutes carried him off. Some jurors thought it
was from the bite of a serpent.
1841, September 15 th. — A man bitten by a snake on the
1849. — A finback whale driven on shore at Colaba, 60 feet
long, 30 to 40 feet round the thickest part. All along the road
from the Fort to Colaba was a perfect fair. . The stench was felt
from the town side of the causeway from where it lay at the
back of Colaba Church. Jawbone taken away. — Gentleman s
Gazette.
1850, Oct. 9th. — A tiger at Bandoop leaped upon the mail-
cart and upset it, and the ghiarry-wallah was little injured. I
saw jackals several times in the gardens of the Colaba Observa-
tory in 1844. — Dr. Buist. On tins Mr. Charles Chambers, F.K.S.,
observes (1893) : " I found a jackal in my bedroom in the
Colaba Observatory about fifteen years ago."
A jackal was killed in the new High Court Buildings shortly
after they were finished.
1858, March 3rd.— Some officers of the P. and 0. steamer
Aden observed a tiger swimming from Mainland to Mazagon.
A boat was lowered and the crew armed with ship's muskets.
When they came up to it the brute was boarding a buggalow,
and was being kept off by the lascars by handspikes. It was
shot through the head by six balls. Weight, 353 lbs. Length
to tip of tail, 8 ft. 9 ins.
1858, May 26th. — A young Portuguese this day shot a tiger
at Mahim, and on the 27th inst. brought the carcass to the
Chief Magistrate for the reward,
1859. — To-day Mr. Forjett with a fowling-piece shot a tiger
within a few hundred yards of the fashionable drive on the
Esplanade, and on the beach of Back Bay near Sonapore. Mr.
Forjett promised the hide to Dr. Birdwood for the Museum.
—Bombay Gazette.
Feb. 6th. — On this day, Sunday evening, the wife of Mr.
Pratt, uncovenanted assistant in the General Department Secre-
tariat, walking along with her husband in the fields adjoining
their residence at Mahim, trod on a snake and died two hours
afterwards. — Bombay Gazette.
Feb. 15th. — ■A tiger was seen sloping about the nooks of
Kalbadavie, but disappeared.
Nov. 12th. — Dr. Turner, P. and 0. service, at his residence,
Chinchpoogly, was bitten by a venomous snake on the calf of
the leg. His leg swelled to an immense size. A friend of his
made an incision, sucked the wound, and he is now recovering.
Kov. 16th. — A cobra, 4 ft. in length, killed in Secretariat
compound, Apollo Street.
1860, Oct. 31st. — On Sunday a snake was seen amusing
itself round one of the pillars in St. John's Church, Colaba, a
few yards from the reading-desk, and not long ago a cobra was
found in the organ. — Times and Standard.
Dec. 5 th. — A hyena shot while devouring a bullock not far
from the Byculla Club House.
1863, Jan. 25th.— Tiger at Mahim, near railway station.
BELOW VIEW OF BOMBAY 1854--
[1]VIEW OF THE WILD DESOLATE LANDSCAPE
FROM SION HILL SHOWING A STEAM TRAIN.
[3]BELOW THE OLD BYCULLA RAILWAY STATION
Past-India
BAZAR GATE AREA, BOMBAY FORT SHOWS HARBOUR BUILDINGS-
A PALANQUIN TAXI,TENTS USED BY SOLDIERS,A WELL WITH WATER WHEEL;MAST OF SHIPS IN HARBOUR,STORAGE GODOWS
|
| A WATER WHEEL ,AS SEEN IN THE PICTURE ,ABOVE USED IN WELLS |
ANOTHER LATER VIEW OF SAME BOMBAY GREEN [HORNIMAN CIRCLE] AREA
Posed group of six figures taken by Hurrichund Chintamon c. 1867, from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections. This photograph was shown at the Paris Exhibition of 1867. The European on the left is identified simply as 'A German', three other figures as 'Parsees', the figure seated on the left as Dr Bhau Dajee, and the figure seated on the right, as 'Shenoy' (?). Parsees are descendants of the Persian followers of Zoroaster who fled to India in the seventh and eighth centuries to escape Muslim persecution.
Panorama of Fort, Bombay--Photographer: Dayal, Deen (1844-1905) Medium: Photographic print Date: 1885
PHOTO SHOWS FORT AND HARBOUR BOMBAY 1850'S ;
THE FIRST STEAM SHIP TO BOMBAY VIA CAPE OF GOOD HOPE-SOUTH AFRICA (BEFORE SUEZ CANAL WAS MADE) 1936
BOMBAY ST.THOMAS CATHEDRAL
Founding Fathers of the city
Sir Jagannath Shankershet, gave of his time and
money for promoting education, political and social
reforms and civic affairs.
Seth Premchand Roychand
Premchand Roychand was a 19th-century Indian businessman known as the "Cotton King" and "Bullion King".
Born in 1831 he was the son of Roychand Dipchand, a merchant from Surat. The Roychand family moved to Bombay when Premchand was a young boy. Recorded as the first Indian broker to speak, read and write English, he entered the lists as a stock broker in 1849. Apart from the capital markets, Premchand Roychand had significant business interests in the cotton and bullion markets along with stock market. He was the founding member of The Bombay Stock Exchange
He reaped enormous profits from the cotton boom that changed Bombay's economy for all times to come. Founder of the Bank of Bombay, people flocked to his Mazgaon mansion when it was illuminated on festive occasions.
Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy
s gifts to the city included
a school of art and a hospital. In 1851 alone, he
made contributions to causes as varied as the
enlarging of a tank, the construction of the J. J.
Obstetric Hospital, a school of Industry and two
roads connecting Mount Mary Church at Bandra
with Mahim Causeway
Sir Cowasji Jehangir
used his millions to gift the
city a Convocation Hall, an Ophthalmic Hospital,
an Art Gallery and 40 drinking water fountains.
He offered his unstinted support towards
education in the city and many educational
institutions owe their existence to his
munificience.
CONTINUED AS PART1B-
PART 2-
PART 3 -
TO PART 12
|


















![PEOPLE OF INDIA PHOTOS: Old Asian Hunting Photos[HUNTING ANIMALS WAS A HOBBY AND SPORTS FOR THE RULERS-BRITISH]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhXRclJsg-kDe0emNar49cYMhP7BwAlI-KoqC7oiyyqpLvduTFx0ugznu7Py-tePELF7qbsZnUsygrkK2cF5yUrXO0UgQHr51-B6UmX414GTjk-8AXV7EviCi5aH0uBng5swG1zy99rIoY/s1600-rw/Chasing+a+Tiger+Across+a+River.jpg)






