Tuesday, September 13, 2011
[PART-1B](BOMBAY)MUMBAI LIFE/PHOTOS/ MAPS/ Names - 1600
[PART-1Ahttp://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/09/1a-bombaymumbai-taxi-1850-to-2001-also_3982.html
[PART-1B
[PART-2]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/glimpses-of-old-bombay-and-western.html
[PART-3]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/glimpses-of-old-bombay-and-western_02.html
[PART-4]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/4glimpses-of-old-bombay-and-western.html
[PART-5]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/dedicated-to-first-city-mumbai-bombay.html
[PART-6]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/6.html
[PART-7]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/6-glimpses-of-old-bombay-and-western.html
[PART-8]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/7.html
[PART-9]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/04/first-anglo-maratha-war-was-first-of.html
[PART 10]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/06/bombay-history-of-cinema-1896-and.html
[part11]http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/06/indian-modes-of-irrigation1874-elephant.html
[PART12] MAPS OF BOMBAY 1843 TO 1954http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/06/maps-of-mumbai-bombay.html
The
flag of Indian Empire from 1879 to 1946. This flag fluttered atop Fort
William in Calcutta and many other public buildings but was seen as a
symbol of oppression by nationalists who were to eventually lead India
to freedom from European rule.
[continuation from 1A]
[continuation from 1A]
Sir Pherozeshah Mehta
fathered
Bombay's municipal charter by writing
the Municipal Act of 1872, helped
found the Central Bank and
established the independent
newspaper, the Bombay Chronicle.
Dadabhai Nawroji
was the first Asian member
of the British Parliament. He lobbied for the
political rights and representation in the British
Administrative services in India. He was the
founder of the Indian National Congress.
Jamsetji Tata
was the founder of the Tata
Industries. He was the pioneer of Iron and Steel
industry in India. He also built the famous Taj
Mahal Hotel.
Sir Dinshaw M. Petit
donated his plot and
bungalow at Parell for the Bai Sakarbai
Dinshaw Petit Hospital for Animals in
1884
Sir David Sassoon
built a synagogue, and established
schools for juvenile delinquents and for technical
education. His son, Albert, built the large Sassoon
dockyard and Colaba between 1872 and 1875. as also
the famous Devid Sassoon Library near the Bombay
University.
Goculdas Tejpal

donated a hospital,
Mulji Jetha
built the largest textile market in the city
Bomanji Wadia,
The Wadia Group is one of the oldest conglomerates of corporate India. It was founded by SirLovji Nusserwanjee Wadia in 1736. Lovji Wadia secured contracts with the British East India Company
to build ships and docks in Bombay in 1736. This, and subsequent
efforts, would result in Bombay becoming a strategic port for the
British colonial undertakings in Asia. The one ship that the Wadias built and of most historic significance for Parsis is the HMS Minden. The Bombay Courier, June 23, 1810 wrote:
“On Tuesday last His Majesty’s Ship, the Minden
built in the new docks (Bombay) by Jamshedji Bomanji Wadia was floated
into the stream at high water, after the usual ceremony of breaking the
bottle had been performed by the Honorable Governor Jonathan Duncan.
mukesh ambani
o------.....---mukesh ambani-........------o
-0--........----Anil ambani-........-----0-
The names of many mercantile magnates and pioneers of industry became synonymous with
the town's life. These included men such as
Sir Dinshaw Petit,
From
his humble beginnings this industrious young man rose to be a captain
of the industry in his homeland of India pioneering the introduction of
several industries. His acts of philanthropy became a legend as he
bankrolled the rescue mission aimed at saving at the remaining small
community of Zarathushtrians in the birthplace of the faith, Iran.
Tatas
have been at the forefront in the making of the Indian nation - not
just by their monumental achievements as industrialists and
entrepreneurs but also by their phenomenal philanthropic contributions
in areas of medical research, higher education, aviation, culture, arts
and human development. This article while highlighting the attributes of
J. R. D. Tata, encapsulates the essence of a 'Century of Trust' built
on the Tata tradition of Charity, Industry and Integrity.
A
socially conscious and visionary lady who despite her family means to
live a lavish life dedicated her life to the service of those less
privileged than herself. She became the first Zarathushti to think of
building affordable homes, offering security for migrant families from
Gujarat in search of a better future in the large metropolitan city of
Bombay.
A
young dynamic Zarathushti lady defies the colonial rule imposed on her
country of birth at great personal risk, and sets the stage for the
eventual independence of India half a century later
Nusserwanji Petit,
Khatau
SETH KHATAU MAKANJI STARTED THE KHATAU GROUP IN 1874;PART OF TEXTILE INDUSTRY OF INDIA
Dharamsey Punjabhai,
James Greaves,
James
Greaves & Company (JGC), an Indian firm that was established in
1858. JGC went into a partnership with George Cotton, an agent of the
East India Company, to set up a venture called Greaves Cotton & Company. In
1927, Crompton & Company merged with F. A. Parkinson, pioneers in
the field of large-scale industrial engineering to form a new company,
Crompton Parkinson. Crompton Parkinson, UK, set up a factory in Worli,
Bombay
George Cotton,
Morarji Goculdas,
Morarjee Goculdas was a textile magnate 1870
Sir Ibrahim Rahimtoola,
A
committed reformer and eminent writer, Ibrahim Rahimtoola was an ardent
champion of the Indianisation of various services. He held very
progressive views in matters of social reform and strongly advocated
female education and abolition of the pardah system. He was a member of
the Bombay Legislative Council (1899-1912) and later its President
(1923-26). He was a member of the Executive Council, Bombay (1918-23)
and Leader of the Bombay Legislative Council (1921-23). He was also a
member of the Imperial Legislative Council (1913-18). He was the
President of the Central Legislative Assembly during 1931-33. A firm
believer in self-government, he advocated constitutional means for
gaining India's Independence.
Thackersey Mulji,
Mancherji Banaji,
Currimbhoy Ibrahim,
Sir (Fazalbhoy) Currimbhoy Ebrahim, 1st Baronet (21 October 1840–26 September 1924) was an Indian Muslim businessman. He wasknighted during the Prince and Princess of Wales's Indian tour of 1905[1] and created a baronet in 1910[2] and further granted lands to support that dignity by the Currimbhoy Ebrahim Baronetcy Act 1913[3] following the precedent set by the Cowasji Jehangir Baronetcy Act.
David Sassoon
and many others. These captains of
industry not only wielded considerable civic and political influence, but also donated
generously towards innumerable charities and public institutions in Bombay.
View from Malabar Hill | View of Breach from Love Grove. |
View of Breach Causeway | View From Belmont. |
View From Belmont. | View from Sion Fort. |
View from Sion Fort. | View from Island of Elephanta. |
View of the Breach Causeway at Bombay.
THE GREAT BREACH
The
only record which survives of large-scale engineering before the
arrival of the Portuguese is that of the remnants of a massive stone
causeway across the Flats on the island of Bombay. These Flats were the
low-lying lands between Dongri and Malabar hills, seperated from the
island of Worli by the Great Breach, through which the sea poured in at
high tide.
PYDHONIE AND UMARKHADI
The Great Breach may have extended almost to Umarkhadi, the creek seperating Bombay from Mazagaon. Occasionally the two would be linked by a shallow creek at the site of the crowded present-day bazaar area of Pydhonie.
Only the name, which means "foot wash", now gives a clue to the fact
that it was once a creek, because this was probably the first piece of
land to be reclaimed from the sea.
Quite as likely, Umarkhadi was also filled in soon after the arrival of the British and joined Mazagaon irretrievably to Bombay. The last story in which Mazagaon appears as a seperate island relates to its occupation by the Sidi of Janjira in 1690-1. He was repelled by a rag-tag navy of fishermen led by the amateur Parsi admiral Rustomji Dorabji.
THE HORNBY VELLARD
Early
efforts at land reclamation concentrated on the small creeks crossing
the northern Flats of Bombay island. Several of these were dammed or
filled in during the eighteenth century. As a result, the areas north
and east of Umarkhadi andMazagaon
were slowly settled in this period. However, the next major reclamation
was due to the closure of the Great Breach north of Cumballa Hill in
1784 by the building of a sea-wall called the Hornby Vellard. The wall allowed reclamation of the Flats and supplied about 400 acres of land for the extension of the crowded inner city. The precincts of Mahalaxmi,Kamathipura, Tardeo and parts of Bycullah were settled.
Arrival Of Indian & Australian Mails At Alexandria EgypT on the way to Bombay 1853
| PIGEON WITH LETTER CONTAINER ON BACK |
| POOR MAN'S PALANQUIN below-Post haste[email of last century] |
| India, Pigeon Post Collection, 1931-41. |
| POst men running with postal articles 1850's picture[ called dawk wallah by english men ;Scinde Dawk was a very old postal system of runners that served the Sindh, The term also refers to the first postage stamps in india the forerunners of the adhesive stamps used throughout India] Darius extended the network of roads across the Persian empire, to enable both troops and information to move with startling speed. At the centre of the system is the royal road from Susa to Sardis, a distance of some 2000 miles (3200 km). At intervals of a day's ride there are posting stations, where new men and fresh horses will be available at any moment to carry a document on through the next day's journey.By this method a message can travel the full distance of the road in ten days, at a speed of about 200 miles a day.other methods of communications in the past were [1]'message whistling' of canary islands[2] 'tom tom' messages by drum beats,[3]fire signal by south american indians[4] smoke signals by north american indians  Read more:http://www.historyworld.net/wrldhis/PlainTextHistories.asp?historyid=aa93#ixzz1I3DbRsDn Read more:http://www.historyworld.net/wrldhis/PlainTextHistories.asp?historyid=aa93#ixzz1I3DOcxXC |
| India postage 1930 - SHOWS THE 'Dak runner'
Pigeons with messages attached.
|
Pigeon Post during 1st world war
 |
| ICE HOUSE AND GREAT WESTERN HOTEL |
late four from J M Gonsalves' 'Views at Bombay'. During the 1820s, institutions for currency production were constructed in various parts of India including Bombay, Benares and Calcutta. These imposing Doric structures can be seen to represent the feeling of growing political power of the English. The Bombay Mint was constructed between 1821and 1829 on the site of the Fort rubbish dump. The architect was John Hawkins of the Bombay Engineers. The building on the right of the picture is the Town Hall.
icture of six 'Native Judges and Officers of the Court of the Recorder, at Bombay', at the beginning of F W Blagdon's book, 'A Brief History of Ancient and Modern India'. According to Blagdon, these drawings 'were taken from life in 1758' and are labelled respectively as holding the following positions. '1. Judge of the Hindoo Law, Antoba Crustnagee Pundit. 2. Interpreter, Rhowangee Sewagee. 3. Hindoo Officer, Lellather Chatta Bhutt. 4. Judge of the Mohomedan Law, Cajee Husson. 5. Officer to the Mooremen, Mahmoud Ackram of the Codjee order or priesthood of the cast of Moormens. 6. Haveldar, or summoning Officer, Mahmound Ismael'.
1838.
Engraving of the Grant Medical College showing part of Sir Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy's Hospital in Bombay by G. R. Sargent from his own drawing and published by him in London in 1844. The engraving was printed by M & N Hanhart. The Grant Medical College and the Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy Hospital were built in the 1840s and funded jointly by Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy and the East India Company. Jamsetjee Jeejeebhoy (1783-1859) was a Parsi merchant and eminent philanthropist. The Grant Medical College is shown in the foreground of this view. It was named after Sir Robert Grant, the Governor of Bombay between 1835 and 1838.
The
idea for the construction of a wet docks for the use of shipping in
Bombay harbour was first suggested by M. Malet when member of Council in
1855. In 1866, Russell Aitken, Executive Engineer to the Municipality
prepared the foundation of a Harbour and Dock Trust which could raise
money for the construction of wet docks on the Elphinstone and Mody Bay
reclamations as private companies had gone into a recession. In 1875,
the first stone was laid in the hope that the new dock would create a
prosperous revolution in the trade of Bombay. In April 1879, the
Prince's Dock was thrown open by the Governor of Bombay, Sir Richard
Temple. In 1884, it was decided to extend the dock and construction then
began on the Victoria Dock.
Photograph
with a view of a carriage on a road lined with palms at Bombay
(Mumbai), Maharashtra, taken by an unknown photographer in the 1870s,
part of the Bellew Collection of Architectural Views. The
area known as Marine Lines at Bombay took its name from the 10th Marine
Battalion of the Bombay Pioneers, composed of Indian troops led by
British officers, which was stationed here in the mid-19th century.

Photograph of a group of pupils from the Juggunath Shankarset Girls' School at Bombay in Maharashtra from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections: India Office Series (Volume 46), taken by an unknown photographer in c. 1873. This image of pupils posed on the verandah was probably shown at the Vienna Exhibition of that year. On the photograph, there is a letterpress caption, above the main caption, which reads "Student's Literary & Scientific Society, founded 1848. President Dr Bhau Daji." S.M. Edwardes wrote in The Gazetteer of Bombay City and Island (3 vols, Bombay (1909-10), "...The Students' Literary and Scientific Society, which supported nine vernacular free schools for girls, attended by 654 pupils, of whom 136 were Marathi-speaking Hindus, 120 Gujarati Hindus and 398 Parsis...The formation of this society was promoted by Professor Patton of the Elphinstone College in 1848. It was intended by the student and assistant teachers of the Elphinstone Institution to be a mutual improvement society and to aid the dissemination of knowledge by means of vernacular lectures and the publication of cheap periodicals in the vernacular languages..
This
view of the Esplanade in Bombay was taken by an unknown photographer in
the 1860s. Originally, Bombay was composed of seven islands separated
by a marshy swamp. It’s deep natural harbour led the Portuguese settlers
of the sixteenth century to call it Bom Bahia (the Good Bay). The
British Crown acquired the islands in 1661when Catherine of Braganza
married Charles II, as part of her marriage dowry. It was then presented
to the East India Company in 1668. The second governor, Gerald Aungier,
developed Bombay into a trading port and centre for commerce and
inducements were offered to skilled workers and traders to move here.
The Esplanade, now an area known as the Maidans, is set behind Marine
Drive on the western side of Colaba Causeway. Before the land on which
Marine Drive was built was reclaimed from the sea, the area formed the
seaside esplanade behind Chowpatty Beach.

Photograph of pupils of the Alexandra Native Girls' Institution at Bombay in Maharashtra from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections: India Office Series (Volume 46), taken by an unknown photographer in c. 1873. This image was probably exhibited at the Vienna Universal Exhibition of the same year. Female education in india grew dramatically in the latter part of the nineteenth century. The Imperial Gazetteer of India states regarding female education, "The Government did not take up the subject until 1849, when Lord Dalhousie informed the Bengal Council of Education that henceforth its functions were to embrace female education, and the first girls' school recognized by Government was founded shortly afterwards by a committee of native gentlemen. The despatch of of 1854 directed that female education should receive the frank and cordial support of Government...The Education Commission of 1882 advised that female education should receive special encouragement and special liberality...The adoption of this attitude has resulted in a considerable development of the public instruction of girls, although it still lags far behind that of their brothers. In 1871 there were 134 secondary and 1,760 primary girls' schools; in 1901-2 the numbers were 461 and 5,628 respectively.
Lithograph of a view of Colaba by Jose M. Gonsalves (fl. 1826-c.1842) plate 3 from his 'Lithographic Views of Bombay' published in Bombay in 1826. Gonsalves, thought to be of Goan origin, was one of the first artists to practice lithography in Bombay and specialised in topographical views of the city. Colaba was originally the southernmost of Bombay's seven islands and named after the Koli fishermen who lived here. The island was visited by the English residents of Bombay for recreation from the 18th century and also used as a military cantonment in the 19th century. Colaba was connected to Bombay by a causeway that was only accessible at low tide by 1838. Within six years, Colaba became the new centre for the cotton trade
Ceremony witnessing the handing of the British Crown from the East India Company to Queen Victoria:-http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010_06_07_archive.html

| INDIANS CARRYING,ON A PALANQUIN- A WHITE WOMAN WITH A WHITE UMBRELLA IN SIMLA MALL(MAIN STREET) 19 TH CENTURY PHOTO.[INDIANS WERE NOT ALLOWED IN THE MALL AREA BY BRITISH RULERS IN THE BEGINNING BUT LATER ON ALLOWED] |
ANTIQUE POST CARD-SCHOOL BOYS AND TEACHER-BOMBAY.THE SCHOOL BOYS ARE USING PALM LEAF BOOKS -IN THEIR HANDS,(PROBABLY VEDA SCHOOL) |
{Palm leaves were first cut from the trees before they could dry up and
become brittle. These were then boiled in water to the required
temperature in order to render them soft. The softened leaves were then
dried in the shade or mild sunshine. The desired portion was taken from
mid-leaf, pressed and then polished. These were then cut into the
required size and made into rolls of paper.Tālapatras or palm leaves of slightly yellow hew, eight angulas (inches) long, which were more brittle and hence cheaper, were given to students for copy work. The leaves of shritāla were a slight red in color and were 24 to 32 angulas in length. These were quite thin, soft and malleable. Such leaves were supplied to poets, scholars and writers.
There were professional palm-leaf paper-makers (ôleya kāyakadavaru) 2, who prepared ready-to-write ôles or palm-leaves, and supplied them to mathas , basadis, temple schools and private individuals. These were sold in rolls ( kāttu) in village shanties as well3.
Specially prepared preservative oil was applied to palm-leaf rolls
before tying them into a book. Turmeric was often used to make the rolls
colorful. Holes were made in the margins of these leaves, through which
silken thread was passed and the leaves were carefully tied, and
finally the book was ready
Palm-leaf Texts

 Scribe
Scribe
Scribe using metal pen to write on dried palm leaves.
A steel pen was used to write on palm leaves
Devanagiri Manuscripts - 9th - 17th Century:

 Bamboo pens - also known as Reed pens used for writing devanagiri
script. The 45 degree cut is the reason for the thick and thin features
of the letterings.
Bamboo pens - also known as Reed pens used for writing devanagiri
script. The 45 degree cut is the reason for the thick and thin features
of the letterings.

1630 AD
 Devanagiri Manuscript of Bhagavata Purana
Devanagiri Manuscript of Bhagavata Purana
Palm-leaf Texts
Scribe using metal pen to write on dried palm leaves. |
A steel pen was used to write on palm leaves
| Devanagiri Manuscripts - 9th - 17th Century: |
| |
1630 AD |
Class with mistress in a mofussil or up-country girls' school, Bombay
Group of Parsee pupils and masters in class of the Elphinstone High School, Bombay --
Photograph
of pupils in a class of the Elphinstone High School at Bombay in
Maharashtra from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections: India
Office Series (Volume 46), taken by an unknown photographer in c. 1873.
This image of pupils gathered around a table conducting an experiment,
possibly in physics, was shown at the Vienna Exhibition of the same
year. The school shown here is named after Mountstuart Elphinstone who
helped to establish the educational structure of the Bombay area. The
Imperial Gazetteer of India states,
"There are three classes of secondary schools - the vernacular and
English middle schools, and the high schools...The English secondary
school stage is divided into middle and high school sections, which
really form portions of the same course...the English school education
should ordinarily be completed by the time the pupil attained the age of
sixteen...In English secondary schools the main course
has hitherto led up to the matriculation or entrance examination of one
or other of the Universities. There are other courses of a more
practical character leading up to different examinations...A purely
literary education has been more popular among both parents and
students, as being in itself more attractive to them and as affording a
better opening for remunerative employment. The
matriculation has generally been accepted as a qualifying test by
Government and private employers as well as by the Universities, and has
been regarded as the common goal of the school career."

A girls' school operating in Jagannath Shankar Seth's residential complex
Jagannath Shankar Shet (10 October 1800 – 31 July 1865), was a notable
Indian Philanthropist and a revolutionary Educationalist. He was born in
1800 in the wealthy Murkute family of Goldsmiths of the Daivadnya Caste
in Mumbai (Bombay). He was one of the founders of Elphinstone College,
and Indian Railway Association that became part of the Great Indian
Peninsula Railway. He was the first Indian member to be nominated to the
Legislative Council of Bombay under the XXTY 26 Act of 1861, a member
of the Bombay Board of Education, and also the first Indian member of
the famous Asiatic Society of Bombay.
Photograph of a group of pupils from the Bhagwandas Purshottum Girls' School at Bombay in Maharashtra from the Archaeological Survey of India Collections: India Office Series (Volume 46), taken by an unknown photographer in c. 1873. This image of pupils posed on the verandah was probably shown at the Vienna Exhibition of that year. On the photograph, there is a letterpress caption, above the main caption, which reads "Student's Literary & Scientific Society, founded 1848. President Dr Bhau Daji." S.M. Edwardes wrote in The Gazetteer of Bombay City and Island (3 vols, Bombay (1909-10), "...The Students' Literary and Scientific Society, which supported nine vernacular free schools for girls, attended by 654 pupils, of whom 136 were Marathi-speaking Hindus, 120 Gujarati Hindus and 398 Parsis...The formation of this society was promoted by Professor Patton of the Elphinstone College in 1848. It was intended by the student and assistant teachers of the Elphinstone Institution to be a mutual improvement society and to aid the dissemination of knowledge by means of vernacular lectures and the publication of cheap periodicals in the vernacular languages..."
Group of mistress and pupils of the Government Normal School, Bombay19TH CENTURY
| Coloured lithograph of the Government House at Parel in Bombay by Day & Son after Sir Harry Francis Colville Darrell (1814-1853) from his 'China, India and the Cape' published in London in 1852. Parel, originally an island, is located in the northern part of Bombay. The building shown in this view was built by the Jesuits[ as a church] under Portuguese rule in the 16th and 17th centuries.Later It was used as a country retreat for the English Governor of Bombay from 1719. In 1829, the building officially became the Government House. However, in the 1880s the Government House was relocated to Malabar Point. |
THE ICE HOUSE':-
BELOW:-
BOMBAY 1850Photograph
from 'Views in the island of Bombay' by Charles Scott,1850s. This is a
view looking north along Apollo Street from the Apollo Gate towards the
dockyards entrance on the right.
The Scotch Church
stands in the left foreground, with Hornby House beyond. The classic
Georgian style Saint Andrew's or Scotch Kirk was completed in 1819.
Hornby House,
which initially began as a residence to the Governor Hornby, served as
the Law Court until the late 1870s when it became the Great Western
Hotel.
Between this building and the church, stands the domed
Ice-House,
erected by subscription in 1843 for the consignments of ice which were
imported regularly and sold to the public. When ice began to be
manufactured in Bombay the Ice-House lost its purpose and was used as a
godown until it was demolished years later.
{ SHOWS
HORSE CARRIAGES AND BULLOCK CART CARRIAGES PARKED NEXT TO COURT
HOUSE;AND A MAN WAITING FOR CUSTOMERS WITH HIS PALANQUIN NEAR CHURCH
STEPS;FORT BOMBAY.
'
-SEEN AS A WHITE ROUND HOUSE AND A WHITE ROUND ROOF}
.The ice-house was a double-shelled structure,twenty-five feet square on
its outside dimension, nineteen feet square on the interior, and
sixteen feet high. It held about 150 tons of ice. ICE WAS HARVESTED
FROM PLACES NEAR TO THE NORTH POLE AND FROZEN LAKES.,BROUGHT BY SHIP
AND KEPT FOR USE. [ELECTRICITY /REFRIGERATION Were NOT YET DISCOVERED].
Once inside, the blocks were piled together as closely as possible to
prevent all unnecessary melting. The workmen in the ice-houses pried
loose the stored ice by means of chisels.Wenham Lake ice enjoyed its
greatest popularity in England between the year 1844 and the early years
of the 185o's. It was in demand everywhere, and it grew into such vogue
that London hotels put up signs informing their customers that Wenham
Lake ice was served there.Main customers were the local coffee-house
owners who bought the ice for the manufacture of their ice-creams.
READ ALSO how ice was brought to Bombay from America by ship:- :-http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/02/how-ice-came-to-india-1833.html
STORY OF ICE AND ICECREAMS IN BOMBAY
BOMBAY:-ICE CAME TO BOMBAY VIA SHIP FROM U.S.A IN 1833
In 1833, fellow Boston-based merchant Samuel Austin proposed a partnership for selling ice to India, then some 16,000 miles and four months away from Massachusetts. On May 12, 1833 the brig Tuscany sailed from Boston for Calcutta, its hold filled with 180 tons of ice cut during the winter. When it approached the Ganges
in September 1833, many believed the delivery was an elaborate joke,
but the ship still had 100 tons of ice upon arrival. Over the next 20
years, Calcutta would become Tudor's most lucrative destination,
yielding an estimated $220,000 in profits.
large crowd of natives gathered at the wharf to witness the unloading of these
"crystal blocks of Yankee coldness."
One of the Indians braved to touch a piece of the ice, and, believing
that he had burned himself, wrapped his hand in his robe and rushed away
followed by a number of the alarmed onlookers. At another time, a
native was supposed to have asked Captain Codman,
"How this ice make grow in your country? Him grow on tree? Him grow on shrub - how he make grow?"
| Bombay's first ice house(ice storage house where ice unloaded from ship was stored) next to the harbour ;seen in the photo as a rounded white dome house;next to the church--1860's photo |
|
"From the insides of this boat they were taking out great pieces of
white stuff, which, in a little while, turned to water. Much split off,
and fell about on the shore, and the rest they swiftly put into a house
with thick walls. But a boatman, who laughed, took a piece no larger
than a small dog, and threw it to me. I - of all people - swallowed
without reflection, and that piece I swallowed as is our custom.
Immediately I was afflicted with an excessive cold which, beginning in
my crop, ran down to the extreme end of my toes, and deprived me even of
speech, while the boatmen laughed at me. Never have I felt such cold. I
danced in my grief and amazement till I could recover my breath, and
then I danced and cried out against the falseness of this world; and the
boatmen derided me till they fell down. The chief wonder of the matter,
setting aside the marvellous coldness, was that there was nothing at
all in my crop when I had finished my lamentings
| VINTAGE ICE CRUSHER |
Developed
for home use in 1848, the traditional crank ice-cream freezer employs a
metal dasher inserted into a metal cylinder full of ice-cream base, which is placed in a bucket filled with a rock-saltand ice mixture (brine). The hand or motor-cranked dashers turn around in the ice-cream mixture as it freezes, preventing icecrystals from forming and ensuring a smooth, creamy final product.
|
 |
| HORSE PULLED ICE AND ICE CREAM CARTS c: 19th century |
| BOMBAY 1900-PARTY |
Falooda
| Kulfi: [India's answer to Gelato] |
| GolaA big ball of ice shavings twinkles like a lump of South African diamonds, kala khatta juice dripping off its sides. Fix it to your lips and slurp away in bliss. |
| This
image shows a water carrier pouring water from a leather bucket into
the leather container slung over the back of a bullock;A Bheestie or Pukkalli [using a bullock - as in this image] is a domestic servant;Bheesties
deliver as many potsful or skinsful as may be needed during the day,
and are paid in proportion. They also serve in the regular army;In
cavalry regiments a Pukkal Bheestie...is also on the establishment of
every troop, in the proportion of one to twenty-five or thirty horses;[Watson and Kaye's 'The People of India', published in eight volumes from 1868 to1875] Many of the best houses in the Bazaar had deep wells of fairly good water within their tenements,but an abundant supply was available for those who had it not from the wells which had been dug outside the walls on the Esplanade,[NEWS OF THE GARRISON OF BOMBAY, 1845. as reported in 1887] READ ALSO:- the first dentist inside bombay fort etc news:-http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2009/02/bombay-firsts-19-th-century-first.html |
FORT BOMBAY WITH FORT WALLS 1850 |
PHOTO BELOW SHOWS:-
THE ORIGINAL CHURCH GATE OF BOMBAY FORT;
 | ||
NAMED CHURCH GATE ; BECAUSE THE GATE WAS NEAR ST.THOMAS CHURCH WHICH CAN BE SEEN IN THE BACK. LATER CHURCH GATE RAILWAY STATION
GOT THIS SAME NAME ;AS IT WAS BUILT NEAR THIS FORT GATE.THE FORT WAS
BUILT AGAINST ENEMIES;SUCH AS PORTUGUESE AND SIDDI SHIPS
THE GATE HAD A BRIDGE BUILT, OVER A MOAT, FILLED WITH WATER ;TO PREVENT ENEMY SOLDIERS;CAN BE SEEN IN THIS PHOTO.THIS FORT AND GATE WERE DEMOLISHED AND Flora Fountain was positioned at the same spot where the Church gate stood before its demolition.
below:- BOMBAY TIMES OFFICE SEEN IN FOREGROUND[second building from the corner]A brief history of The Times
1838: The first edition appears on November 3, 1838, known as The Bombay Times and Journal of Commerce.
The newspaper was published twice a week under editor J.E. Brennan. It
is basically a city paper reflecting the interest of Bombay's business
community.[12]
1846-1857: The newspaper changes hands and George Buist, LL.D, F.R.S., becomes the editor of the Times from 1840-57.[13]
1850: Shareholders decide to increase the share capital and the paper is converted into a daily.[14]
1859: Bombay Standard and Chronicle of Western India merges into The Bombay Times and Journal of Commerce to form Bombay Times & Standard[15]
1861: Editor Robert Knight amalgamates The Bombay Times & Standard and Bombay Telegraph & Courier to form The Times of India and gives it a national character.[12]
1880: The Times of India Weekly Edition is launched name later changed to The Times of India Illustrated Weekly and finally to The Illustrated Weekly of India in 1923.[16]
Church Gate Street, Bombay.Photographer: Unknown Medium: Photographic print Date: 1860
CHURCH
GATE =THE GATE OF THE BOMBAY FORT ; NEAR TO ST THOMAS CATHEDRAL
CHURCH,SEEN AT FAR END [THE FORT HAD MANY SIMILAR GATES ;The fort walls
had three main gates. One was the Apollo Gate, near the present day
location of the St. Andrew's Church. The most well-known was Church Gate, named after St. Thomas', standing almost exactly on the spot that the Flora Fountain
now occupies. The third was the Bazaar Gate, right opposite the present
dome of the General Post Office, which lends its name to the area even
now, long after the gate itself has disappeared.]
This view of Churchgate Street, now known as Vir Nariman Road, in the Fort area of Bombay was taken in the 1860s to form part of an album entitled 'Photographs of India and Overland Route'. Churchgate Street runs from Horniman Circle at the east end to what was originally named Marine Drive at the edge of the Back Bay. Churchgate Station, the old General Post Office (now the Telegraph Office) and the Cathedral Church of St Thomas, the oldest still-functioning structure in the city, are all located along its length. However, Churchgate Station and the Post Office were later additions to the street and would not have been in existence at the time of this photograph. In 1772 an order was promulgated to segregate Indian and English houses, both within and outside the Fort. A more important development came five years later, in 1777, when the first newspaper in Bombay was published |
also read ABOUT HARVESTING OF ICE FROM FROZEN LAKES AND FIELDS FOR EXPORT TO FAR OFF PLACES INCLUDING INDIA 1850'S>> :-http://www.iceharvestingusa.com/Frederic%20Tudor%20Ice%20King.html
http://www.iceharvestingusa.com/crystalblocks1.html
when the natives on Bombay first saw the ice being unloaded from ice barges:-
when the natives on Bombay first saw the ice being unloaded from ice barges:-
"From
the insides of this boat they were taking out great pieces of white
stuff, which, in a little while, turned to water. Much split off, and
fell about on the shore, and the rest they swiftly put into a house with
thick walls. But a boatman, who laughed, took a piece no larger than a
small dog, and threw it to me. I - of all people - swallowed without
reflection, and that piece I swallowed as is our custom. Immediately I
was afflicted with an excessive cold which, beginning in my crop, ran
down to the extreme end of my toes, and deprived me even of speech,
while the boatmen laughed at me. Never have I felt such cold. I danced
in my grief and amazement till I could recover my breath, and then I
danced and cried out against the falseness of this world; and the
boatmen derided me till they fell down. The chief wonder of the matter,
setting aside the marvelous coldness, was that there was nothing at all in my crop when I had finished my lamenting s."
| THE LONG LONG (HOT ) DAY IN AN ENGLISH MAN'S LIFE IN INDIA |
| BOMBAY
1880'S BEFORE DISCOVERY OF AUTO MOBILES-(CARS) SHOWS HORSE
(PULLED)TRAMS AND HORSE CARRIAGES AT FLORA FOUNTAIN.. IT SEEMS THE ROADS
ARE SPRINKLED WITH WATER ,ON THE LEFT SIDE ,TO PREVENT DUST CLOUDS
FROM ROAD;USING BULLOCK CARTS AS SEEN IN PHOTO HORSE DRAWN TRAMS;HORSE CARRIAGES,BULLOCK CARTS ALSO SEEN |
Bhendi Bazaar was a bustling commercial area of the city,
| A horse-drawn tram on colaba causeway. The offices and stables of the Tramway Company is beside the Wesley Church, with the original steeple. A bus depot and the Electric House building replaced the Tramway Company office |
THE TAJ MAHAL PALACE HOTEL ENTRANCE.

foot pedal fan before electricity Bombay kalbadevie road  |
Bombay,[BULLOCK CART FOR PASSENGERS] a photo by Francis Frith, c.1870'
 |
| BOMBAY STREET SCENE 1900'S |
http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2010_07_06_archive.html |
-BOMBAY-FLORA FOUNTAIN;SHOWING HORSE CARRIAGEcollotype by Clifton & Co., c.1900; * overview of theTAXI |
| TOWN HALL 1850'S PHOTO |
| PHOTO OF TOWN HALL BOMBAY |
| PHOTO OF V.T.(VICTORIA TERMINUS RAILWAY STATION) NOW NAMED C.S.T (CHATRAPATI SHIVAJI TERMINUS)STATION;NO CARS -ONLY HORSE POWERED TRAMS;CARRIAGES;BULLOCK CARTS.C: 1880 |
*"Scene in Bombay
| ANDHERI RAILWAY STATION C: 1870'S--[AND FOX HUNT] BY ENGLISH MEN AROUND THE RAILWAY STATION[ A DESOLATE RAILWAY STATION BUILDING CAN BE SEEN IN THE MIDDLE OF WILDERNESS |
1853

On April 16th, at 3:35pm, the first train in India leaves Bombay for Thane
STEAM ENGINE TRAIN IN USA
goa railway station and steam engine
THERE WERE MANY STEAM ROAD ROLLERS AND STEAM BUSES CAN BE SEEN IN NEHRU SCIENCE MUSEUM MUMBAI
some steam road rollers saved from scrap yard- in India:-
| Make |
|---|
| Mileage | 1 km |
|---|---|
| Year | 1921 |
| Steering | Left |
| Place of Origin | Delhi, India |
A steam road roller at Birla Industrial and Technological museum calcutta
|
BOMBAY - CHURCH GATE RAILWAY STATION--1910's
BELOW :- PHOTO OF BANDRA -1850'S FOX HUNT
![[flora+fountain.jpg]](https://2.bp.blogspot.com/_iZMWbgTP0b4/SZ23u9AbXUI/AAAAAAAABUw/xWi8AEZJdq0/s640-rw/flora%2Bfountain.jpg)

Sindh Police in 1857
fashions;drinks;cigars,road rules etc of life in Bombay fort:-
HORSE CARRIAGES WAITING IN FRONT OF TAJ MAHAL HOTEL BOMBAY
BOMBAY CLUB1880'S
BELOW -WATSON [LUXURY ]HOTEL BOMBAY
ADELPHI HOTEL BOMBAY
BELOW PHOTO 1880'S-METRO THEATER AREA? CARS YET TO BE BORN!
ONLY HORSE CARRIAGES AND TRAMS
| DOMED ICE HOUSE SEEN BETWEEN COURT AND CHURCH |
BELOW BOMBAY VICTORIA MEMORIAL RAILWAY STATION (NOW C.S.T. STATION)-B.C. [MEANS BEFORE CARS-1890'S ]
]
1896-FILM:-
"Embarking elephants at Bombay for the Abyssinian expedition," from the Illustrated London News, 1868: very large scans of the *left half* and the *right half* of the engravin
"Embarking elephants at Bombay for the Abyssinian expedition," from the Illustrated London News, 1868: very large scans of the *left half* and the *right half* of the engravin
BELOW:-"KALA GHODA"STATUE;SEEN STANDING IN FRONT OF SASSOON LIBRARY AND Elphinstone College
{Kala Ghoda (Marathi: काळा घोडा) is a precinct or district in South Mumbai, India.
The name means Black Horse, a reference to a black stone statue of King Edward VII (as the then Prince of Wales) mounted on a horse it was actually build by the famous Jewish businessman and the greatest person who contributed a lot to the city of mumbai Sir David Sassoon who owned Most of the property of this area later also a Library and a lane named after him . Although this statue was removed in 1965 to storehouses of the Bhau Daji Lad Museum (formerly the Victoria & Albert Museum (Mumbai)) in Byculla, Central Mumbai, the name persists. The statue is now in the Jijamata Udyan in Byculla.}
"The Plague in Bombay: House to House Visitation,BY DOCTOR" from the Illustrated London News, 1898 (with modern hand coloring)
kala Ghoda statue
BELOW -STANDING IN MIDDLE OF ROAD IS THE BOMBAY POLICE MAN

PYDOWNIE STREET/MOHAMMED ALI ROAD. Most popular for all-night eating during the fasting month of Ramadan, the congested
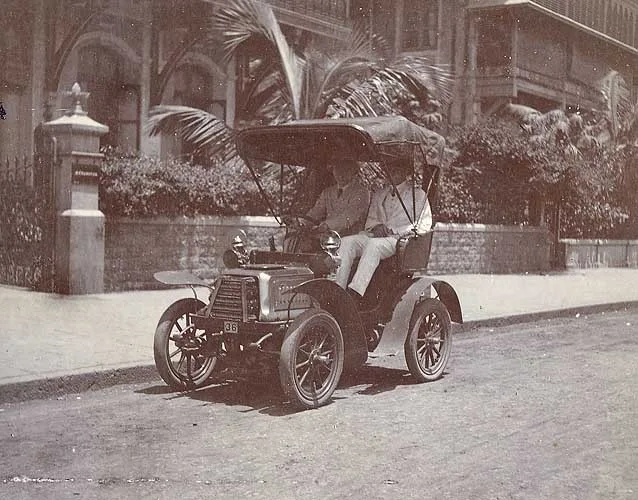
1902 CAR IN BOMBAY:-[cars were originally called as 'horseless carriages']
Sir (Rustomjee Cowasjee Cursetjee) Jamsetjee Jejeebhoy, 5th Bt; Sir Charles William Cayzer, 1st Bt; Miss Cayzer; Miss Jejeebhoy; Sir Jamsetjee Manockjee Cursetjee Jejeebhoy, 4th Bt-1902[BEware of photo hacker-ww.npg.org.uk
Miss Cayzer; Sir Jamsetjee Manockjee Cursetjee Jejeebhoy, 4th Bt; Miss Jejeebhoy; Sir (Rustomjee Cowasjee Cursetjee) Jamsetjee Jejeebhoy, 5th Bt
CARS CAME TO INDIA IN 1898.THIS CAR NUMBER PLATE-REG:NO: 36-[-MAY BE THE 36TH CAR IN INDIA ]
History -- Early years[The first speed limits in the United Kingdom were set by a series of restrictive Locomotive Acts (in 1861,The 1865 (the 'red flag act') reduced the speed limit to 4 mph (6 km/h) in the country and 2 mph (3 km/h) in towns and required a man with a red flag or lantern to walk 60 yards (50 m) ahead of each vehicle, and warn horse riders and horse drawn traffic of the approach of a self-propelled machine;1904Under the Motor Car Act every road going vehicle had to be registered; cars and bikes had to carry front and rear registration plates
The London to Brighton Veteran Car Run 2010
 |
| SARDAR MIR ALI BAHDUR THE FIRST DETECTIVE OF POLICE OF BOMBAY IN 19TH CETURY |
'GATE WAY OF INDIA' BUILT HERE LATER; ALSO (PHOTO BELOW)
http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/02/old-postcards-of-bombay-mumbai.html
OFFICER SITS ON HAND PULLED RICKSHAW;
Rickshaw pullers playing cards 19 th century
A 1905 Humber car , photographed in Bombay-(ONE OF THE FIRST CARS IN BOMBAY)
FIRST FLEET OF TAXI CARS IN BOMBAY 1910;THE PASSENGER SAT IN THE COVERED CABIN WHILE THE TAXI DRIVER SAT IN THE OPEN FRONT ;JUST SAME ARRANGEMENT AS A HORSE CARRIAGE

TAXIS IN NEW YORK 1914-SIMILAR 20 CARS WERE IMPORTED FOR USE AS TAXI IN INDIA ;MAINLY FOR CALCUTTA,BOMBAY
Mr Jinnah on a car ride with a Parsi friend
. Jinnah's friend here is Pestonjee H J Rustomjee and the child is Homi Rustomjee.
NEW CAR SHOW ROOM 1910

DE DION BUTON CAR-1912-cars mostly handle start;self starting cars were made from 1912 onwards

THE MAN STARTING HIS CAR ; (BY CRANKING THE STARTING HANDLE WAS THE ONLY WAY ,BEFORE SELF STARTER WAS DISCOVERED)
DE DION BUTON CAR-1912-cars mostly handle start;self starting cars were made from 1912 onwards
THE MAN STARTING HIS CAR ; (BY CRANKING THE STARTING HANDLE WAS THE ONLY WAY ,BEFORE SELF STARTER WAS DISCOVERED)
CARS 1920 CALCUTTA
MAHATMA GANDHI ;NEAR CAR 1930'S
1920 -30 TAXI CARS ;NO CARS WERE MADE IN INDIA THOSE DAYS .SO ALL CARS WERE IMPORTED FROM AMERICA BRITAIN FRANCE OR GERMANY [.JAPANESE CARS BECAME POPULAR AFTER 1960]
CAR 1920-CROSSLEY
below :- flora fountain 1920's

cars on the road in india- THERE WAS NO 'A' OR 'B' OR 'C' JUST THE NUMBER FOR THE CAR--SEE BELOW THE CAR REGISTRATION NO: JUST '26903'.THIS WAS WHEN NUMBER OF CARS WERE VERY FEW-PHOTO OF CALCUTTA 1930'S
 |
| ENGLISH SOLDIER'S MESS IN COLONIAL INDIA (BEFORE ELECTRICLIGHT CAME),WITH GAS LIGHT AND OVERHEAD HAND OPERATED PUNKAH(FAN) |
EQUAL TO THE SLAVE OAR PULLERS OF ANCIENT ROMAN SHIP ;WHO HAD TO ROW AND ROW FOR HOURS
THE PUNKAH BOY-PULLING THE PUNKAH-FAN
| A vintage 3 coach EMU rake in the early 1940's. (R Harish Kumar) |
Bombay Electric Supply & Tramways Company Limited was a sole provider of electric supply, electric tram service and buses in the Mumbaicity from 1905 to till 1947 when it was municipalised to form the Bombay Electric Supply and Transport Undertaking. [BELOW PHOTO OF B.E.S.T.BUS 1920'S;AND B.E.S.T.'S SINGLE DECKER AND DOUBLE DECKER TRAMS,]
private taxi van 1930's [SEE THE BOMBAY REGISTRATION NO: B.M.B.210]
AND BUS1930'S
MARRIAGE TAXIS[OPEN HOOD CARS];HIRED ALONG WITH BAND WAS COMMON
One of the earliest emu trainsets (4-car ) speeding over the Sandhurst Road flyover
| used on the ghats in 1863 |
Bombay VT with an unidentified train in 1904
colaba station[COLABA STATION AND RAILWAY LINE IS NOW EXTINCT.LAST STATION ON THIS LINE IS CHURCH GATE]
http://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/02/travel-by-ship-before-1960-bombay-to.htmlhttp://oldphotosbombay.blogspot.com/2011/02/travel-by-ship-before-1960-bombay-to.html
1940'S TAXI CARS
MAHATMA GANDHI ENTERING CAR -1940'S PHOTO
1940 -CHEVEROLETCARS
Chandi Das (1934)HINDI FILM
Singer(s): Saigal K L, Uma Shashi
Movie: Dharti Mata (1938) Music: Pankaj Mullick Singers: Krishna Chandra Dey, Uma Shashi & K.L. Saigal
Duniya Rang Rangili
Guzar Gaya Woh Zamana (Pankaj Mullick)
A rare photo of all the singers together in the early years of their singing careers ! Can you spot ( front row) Zohra Jan, Rajkumari, Amirbai Karnatki, Hamida Banu, Geeta Roy (later Geeta Dutt), Lata Mangeshkar, Meena Kapoor, (and standing behind) Sailesh Mukherjee, Talat Mahmood, Dilip Dholakia, Mohd. Rafi, Shiv Dayal Batish, G.M. Durrani, Kishore Ganguli (later Kishore Kumar), and Mukesh.
Zohrabai Ambalewali or Zohrajaan Ambalewali, a very talented and popular singer of yesteryears, is best remembered now by the songs like 'Ankhiyan milage jiyaa bharmaake' and 'Aai Diwali, aai Diwali' sung under the baton of Naushad for the superhit musical film Rattan (1944). Zohrabai Ambalewali was one of the leading playback singers with Shamshad Beghum and Rajkumari till the year 1946-1947. With the arrival of younger and fresher voices like Geeta Roy and Lata Mangeshkar, Zohrabai couldn't hold her position due to their competition. She did not get to sing many songs post the years 1953-1954.
RATAN (1944)
Stars:
Swaran Lata, Karan Dewan and Amir BanuSoundtracks "Ankhiyan Milake"
Sung by Zohrabai Ambalawali
Music composed by Naushad
Lyrics by D.N. Madhok
SHEHNAI - AANA MERI JAAN SUNDAY KE SUNDAY-1947
SINGERS : CHITALKAR & MEENA KAPOOR
Awaz de kahan hai - Noor Jehan
Raat Ne Kya Kya Khwaab Dikhaaye Talat Mahmood in Ek Gaon Ki Kahani
Cast: Talat Mahmood, Mala Sinha,I S Johar, Bipin Gupta, Abhi Bhattacharya, Nirupa Roy, Lalita Pawar,
LATA MANGESHKAR AND MUKESH- LIVE - Kabi kabi
KISHORE KUMAR LIVE-MERE SAPNO KI RANI
KISHORE KUMAR LIVE-MERE SAPNO KI RANI
Geeta Dutt - Jaane Kya Tune Kahi - Pyaasa [1957]
Mera sundar sapna beet gaya-
Artist Biography
Geeta Dutt (born Geeta Roy) was one of the most influential vocalists in the history of Indian cinema. During the ten years that she was in her prime (1947-1957),
Geeta Dutt
do bhai--mera sundar sapna beet gaya
ANMOL GHADI 1946 socha tha kya kya ho gaya Suraiyya
Amirbai Karnataki&Lata-Gore Gore O Baanke Chhore -Samadhi 1950
shamshad Begum - Kabhi Aar Kabhi Paar - Aar Paar [1954]
Talat Mahmood & Shamshad Begum - Milte Hi Ankhen Dil Hua - Babul [1950]
Shamshad Begum - Chaman Mein Reh Ke Veerana - Deedar [1951]
1940-50 BOMBAY MARINE DRIVE

,+India%3B+about+1950.jpg)
1942 FORD JEEP AS TAXIS WERE USED FOR HILLY TERRAIN
1944 FORD VAN WITH WOODEN BODY
1944 FORD MILITARY TRUCK WERE CONVERTED TO CIVIL LORRIES AND WERE USED AS BREAKDOWN TRUCK IN BOMBAY TILL 2000
1945 FORD WAS VREY POPULAR AS PRIVATE CAR AND AS TAXIS TILL 1980
BELOW (THE POPULAR) FORD CAR 1948 -USED FOR WEDDINGS AND AS TAXI
AND 1946 FORD VAN WITH WOODEN BODY
BOMBAY TAXI BMT 1800-C.1950'S

PONTIAC CAR[MADE IN AMERICA] AS TAXI

HILLMAN MINX MADE IN BRITAIN WAS VERY POPULAR AS TAXI IN BOMBAY TILL 1970


Dilip kumar,Dev anand and Raj kapoor with shri Jawahar lal Nehru .
below:-Hillman minx taxi of Bombay 1950

AUSTIN A40 TAXI CAR [MADE IN ENGLAND]

THE FIRST CAR TO BE CONVERTED INTO A INDIAN CAR--MORRIS MINOR ENGLAND WAS MADE INTO HINUSTAN CAR 1950-SEEN BELOW
 MORRIS MINOR(LATER RENAMED BAY HINDUSTAN) TAXI CAR C.1950'S
MORRIS MINOR(LATER RENAMED BAY HINDUSTAN) TAXI CAR C.1950'S
BABY HINDUSTAN CAR-FIRST CAR TO BE MADE IN INDIA [COPIED FROM MORRIS MINOR ENGLAND]C.1950

ANOTHER CAR WHICH WAS CONVERTED INTO AN INDIAN CAR-MORRIS OXFORD INTO HINDUSTAN LAND MASTER

AND LATER INTO AMBASSADOR-SEE BELOW

1956 FIAT MILLICENTO ALSO KNOWN AS DUKKER FIAT -USED AS TAXI IN 1960'S

BMC (BOMBAY)7921


LATER MODEL FIAT -KNOWN AS PREMIER PADMINI BELOW

1960 Tata Mercedez Benz trucks in India

STANDARD CARS MADE IN MADRAS (CHENNAI) CALLED HERALD / TRIUMPH; A FEW USED AS TAXIS IN SOUTH INDIA

ENGLISH MAN'S LIFE IN INDIA 1850'S
PONTIAC CAR[MADE IN AMERICA] AS TAXI
HILLMAN MINX MADE IN BRITAIN WAS VERY POPULAR AS TAXI IN BOMBAY TILL 1970
!
Dilip kumar,Dev anand and Raj kapoor with shri Jawahar lal Nehru .
below:-Hillman minx taxi of Bombay 1950
AUSTIN A40 TAXI CAR [MADE IN ENGLAND]
THE FIRST CAR TO BE CONVERTED INTO A INDIAN CAR--MORRIS MINOR ENGLAND WAS MADE INTO HINUSTAN CAR 1950-SEEN BELOW
Yeh Hai Bombay Meri Jaan - 1958 (Roberto Rossellini)
TAXI DRIVER (1954) HINDI MOVIE[ACTORS DEV ANAND AND KALPANA KARTIK-LATER THEY GOT MARRIED IN REAL LIFE]BABY HINDUSTAN CAR-FIRST CAR TO BE MADE IN INDIA [COPIED FROM MORRIS MINOR ENGLAND]C.1950
ANOTHER CAR WHICH WAS CONVERTED INTO AN INDIAN CAR-MORRIS OXFORD INTO HINDUSTAN LAND MASTER
AND LATER INTO AMBASSADOR-SEE BELOW
1956 FIAT MILLICENTO ALSO KNOWN AS DUKKER FIAT -USED AS TAXI IN 1960'S
BMC (BOMBAY)7921
LATER MODEL FIAT -KNOWN AS PREMIER PADMINI BELOW
1960 Tata Mercedez Benz trucks in India
STANDARD CARS MADE IN MADRAS (CHENNAI) CALLED HERALD / TRIUMPH; A FEW USED AS TAXIS IN SOUTH INDIA
ENGLISH MAN'S LIFE IN INDIA 1850'S
Main Bambai Ka Babu Naam Mera Anjana - Mohd.Rafi
Yeh Hai Bombay Meri Jaan CID
Ee Hai Bambai Nagariya Tu Dekh Babua - Kishore Kumar
BAMBAI SE AAYA MERA DOST - AAP KI KHATIR 1977
Yeh Bombay Sheher - Haadsaa
Bam Bam Bambai - Govinda, Juhi Chawla, Swarg Song
Bombay Theme - AR Rahman
ISKI TOPI USKE SER,USKI TOPI" MOHD.RAFI SHUMSHAD- BEGUM
Bombai Ka Babu - Dekhne Mein Bhola Hai
Miss Bombay (1957): Le chala jidhar ye dil nikal padey
Bach Ke Balm Chal Ke Rasta Hay Mushkil - Jhonny Walker - Rafi
Babuji Dheere Chalna
Chakke Mein Chakka song - Brahmachari
BAMBAI HAMARI BAMBAI,YE RAJ DULARI BAMBAI"BY MOHD.RAFI,M.D:SOORAJ-"STREET SINGER
Worli ka naaka, Do Ustad
Kya Ye Bombai Hain- Ye Bombay shehar ka
The Jetliners - Mignonne - Bombay merry hi
Verse
Come from England, come from Scotland, come from Ireland
Come from Holland, come from Poland, come from any land,
If you're looking out for a pleasant holiday,
Come to Bombay, come to Bombay, Bombay meri hai.
Chorus
Bom bom bom bom
Bombay meri hai
Born bom bom bom
Bombay meri hai
Our ladies are nice, they are so full of spice
Come to Bombay, come to Bombay Bombay meri hai.
Wear a dhoti, put a topi and a small coatie
Mini or bikini is so good for you honey
If you ain't so gay then you can live the sadhu way
Come to Bombay, come to Bombay Bombay meri hai.
Verse
Puri bhaji, bhelpuri you can try and tell
Idli dosa, hot samosa you will like it well
Once you come to stay then you won't like to go awayCome to Bombay, come to Bombay Bombay meri hai.
THAT WAS BEFORE BOMBAY BECAME MUMBAI/MUMBAY.NOW THERE ARE MANY RESTRICTIONS PUT BY POLITICAL PARTIES;SINGING IN RESTAURANTS ARE DISCOURAGED BY VERY HEAVY EXTRA TAXES!!MANY SIMILAR RESTRICTIONS AND SCARE TACTICS MADE OLD BOMBAY INTO MUM BAI OR MUM BAY
{Mum" is a Middle English word meaning "silent".}
Come from England, come from Scotland, come from Ireland
Come from Holland, come from Poland, come from any land,
If you're looking out for a pleasant holiday,
Come to Bombay, come to Bombay, Bombay meri hai.
Chorus
Bom bom bom bom
Bombay meri hai
Born bom bom bom
Bombay meri hai
Our ladies are nice, they are so full of spice
Come to Bombay, come to Bombay Bombay meri hai.
Wear a dhoti, put a topi and a small coatie
Mini or bikini is so good for you honey
If you ain't so gay then you can live the sadhu way
Come to Bombay, come to Bombay Bombay meri hai.
Verse
Puri bhaji, bhelpuri you can try and tell
Idli dosa, hot samosa you will like it well
Once you come to stay then you won't like to go awayCome to Bombay, come to Bombay Bombay meri hai.
THAT WAS BEFORE BOMBAY BECAME MUMBAI/MUMBAY.NOW THERE ARE MANY RESTRICTIONS PUT BY POLITICAL PARTIES;SINGING IN RESTAURANTS ARE DISCOURAGED BY VERY HEAVY EXTRA TAXES!!MANY SIMILAR RESTRICTIONS AND SCARE TACTICS MADE OLD BOMBAY INTO MUM BAI OR MUM BAY
{Mum" is a Middle English word meaning "silent".}
1 comment:
- i heart u said...
- Hello there.
I didnt know where to leave a text so just posting on the comments board. I am working on a period film based in bombay 1950's-1960's and your research will be of great help to us. Please leave me a mail with some contact details so that i can detail things for you. thanks
dhara.jain13@gmail.com -
April 19, 2012 at 9:29 PM
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)







+(6).jpg)

